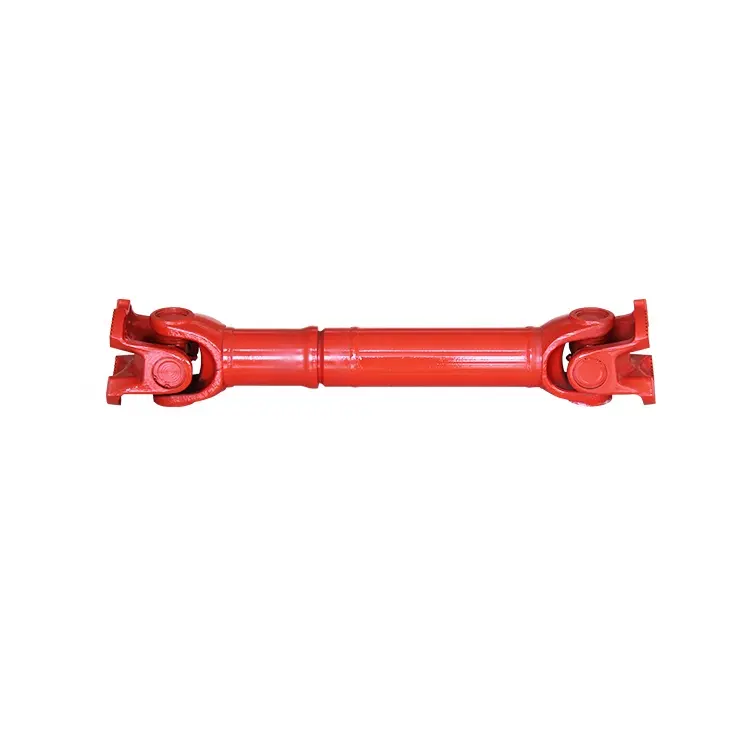
Product Description
PROPELLER SHAFT manufacturer & supplier – CHINAMFG is your best choice
|
Product Name: |
Front Driveshaft Auto parts for Dodge CHINAMFG 65-9483 1997-1999 Drive Prop Shaft |
|
OE NO.: |
65-9483 |
|
Vehicle Fitment: |
For Dodge CHINAMFG 1997-1999 |
|
Delivery Time |
1-7 days for stock items, 45 days for production items |
|
Material: |
High Quality Steel |
|
MOQ: |
1pc if we have in stock |
|
Note: |
Have stock in China and US! |
For DODGE Propeller Shaft, we have over 1
52123110AA
5215714AA
P52853641AD
52088046
52123110AB
5215714AB
52105871AC
5257103
52123110AC
5215714AC
52105860AB
5257104
52123111AA
5215714AD
52105871AB
5257121
52123111AB
5215714AE
5215716AB
530 0571 8
52123111AC
5215714AF
15113831
5305711
52123112AA
5215711AC
15763590
53AA
5215712AA
53AA
5215712AB
906415716
6857187
52123197AB
5215712AC
52853363AD
52123202AA
5215710AA
4593857AB
52853363AE
52123202AC
5215710AB
4593857AC
52853363AF
52123326AA
52123571AA
4593857AD
52853364AB
52123326AB
52123571AB
5104083AA
52853364AC
52123326AC
52123571AC
5104084AA
52853364AD
52123327AA
52123571AD
5119086AA
52853364AE
52123327AB
52123571AE
5157AF
52123993AA
5215710AF
5157AB
52129112AA
5215712AA
5157AB
5215712AB
52088046AB
680 0571 7AA
52853038AC
5215712AC
5257104AB
68AB
5215712AD
521 0571 1AB
6857187AA
52853363AB
5215712AE
521 0571 1AC
6857101AA
52853363AC
5215712AF
52105840AA
68234348AA
5215710AA
5215712AG
52105840AB
P52105871AB
5215710AB
5215710AC
52105860AA
5215710AE
5215716AA
5215710AD
If you need more information about DODGE Propeller Shaft, please message or email to us ASAP.
—- OUR ADVANTAGE —-
+700 models for AMERICA & EUROPE marketMOQ: 3PCS / for 1 item, MIN order amount: USD5000
Quality assurance: One Year WarrantyStable delivery time: 45 days
Free Sample DevelopedApply O/A 30-90 days for regular customer
Becides DODGE Propeller Shaft,we have Over 700 items applicable for following vehicles:
—- F A Q —-
Q1: If we don’t find what we need on your website, what should we do?
You can send us the OE number or of the product you need, we will check if we have them.
We also develop new models according to customer’s need;
you can contact us for more detail.
Q2: Can I get a price discount if I order large quantities? Yes, it depends on your purchasing quantity, more quantity more discount.
Q3: What about the delivery time? If we have stock, we can send you the goods within 3 working days,
if we don’t have stock, generally it needs 10 to 40 days.
Q4: What’s our MOQ? Sample order for quality testing 1 piece , normal order 50 pieces for 1 order with mixed models .
Q5: What’s your payment terms and condition ? We can accept T/T , LC, Trade Assurance, Western Union, Paypal, Moneygram ect.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Dodge |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
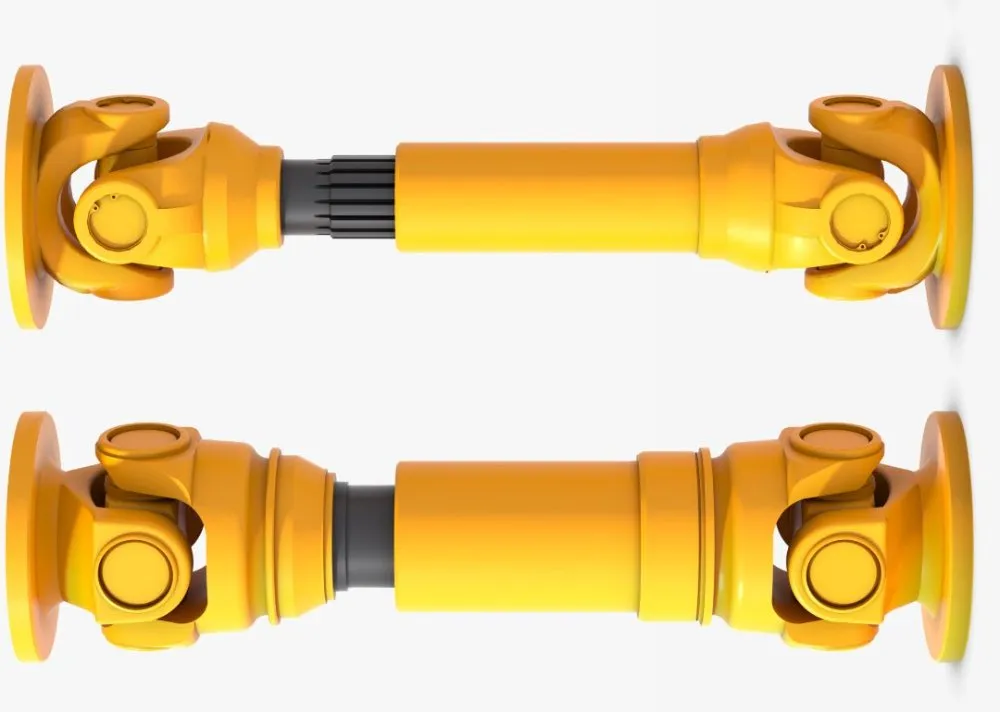
How do cardan shafts handle variations in length and connection methods?
Cardan shafts are designed to handle variations in length and connection methods, allowing for flexibility in their installation and use. These shafts incorporate several features and mechanisms that enable them to accommodate different lengths and connection methods. Let’s explore how cardan shafts handle these variations:
1. Telescopic Design:
– Cardan shafts often employ a telescopic design, which consists of multiple sections that can slide in and out. These sections allow for adjustment of the overall length of the shaft to accommodate variations in distance between the driving and driven components. By telescoping the shaft, it can be extended or retracted as needed, ensuring proper alignment and power transmission.
2. Slip Yokes:
– Slip yokes are components used in cardan shafts that allow for axial movement. They are typically located at one or both ends of the telescopic sections. Slip yokes provide a sliding connection that compensates for changes in length and helps to maintain proper alignment between the driving and driven components. When the length of the shaft needs to change, the slip yokes slide along the shaft, allowing for the necessary adjustment without disrupting power transmission.
3. Flange Connections:
– Cardan shafts can utilize flange connections to attach the shaft to the driving and driven components. Flange connections provide a secure and rigid connection, ensuring efficient power transfer. The flanges are typically bolted or welded to the shaft and the corresponding components, such as the transmission, differential, or axle. Flange connections allow for easy installation and removal of the cardan shaft while maintaining stability and alignment.
4. Universal Joints:
– Universal joints, or U-joints, are essential components in cardan shafts that allow for angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. They consist of a cross-shaped yoke and needle bearings at each end. The universal joints provide flexibility and compensate for variations in angle and alignment. This flexibility enables cardan shafts to handle different connection methods, such as non-parallel or offset connections, while maintaining efficient power transmission.
5. Splined Connections:
– Some cardan shafts employ splined connections, where the shaft and the driving/driven components have matching splined profiles. Splined connections provide a precise and secure connection that allows for torque transmission while accommodating length variations. The splined profiles enable the shaft to slide in and out, adjusting the length as needed while maintaining a positive connection.
6. Customization and Adaptable Designs:
– Cardan shafts can be customized and designed to handle specific variations in length and connection methods based on the requirements of the application. Manufacturers offer a range of cardan shaft options with different lengths, sizes, and connection configurations. By collaborating with cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers, engineers can select or design shafts that match the specific needs of their systems, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
In summary, cardan shafts handle variations in length and connection methods through telescopic designs, slip yokes, flange connections, universal joints, splined connections, and customizable designs. These features allow the shafts to adjust their length, compensate for misalignment, and establish secure connections while maintaining efficient power transmission. By incorporating these mechanisms, cardan shafts offer flexibility and adaptability in various applications where length variations and different connection methods are encountered.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with cardan shafts?
Working with cardan shafts requires adherence to certain safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Whether during installation, maintenance, or repair, it is essential to follow these safety guidelines:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
– Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with lubricants or chemicals.
2. Training and Familiarity:
– Ensure that personnel working with cardan shafts are adequately trained and familiar with the equipment and procedures involved. They should understand the potential hazards, safe operating practices, and emergency procedures.
3. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
– Before working on cardan shafts, follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to isolate and de-energize the equipment. This prevents accidental activation or movement of the shaft while maintenance or repair activities are being performed.
4. Secure the Equipment:
– Before starting any work on the cardan shaft, ensure that the equipment or vehicle is securely supported and immobilized. This prevents unexpected movement or rotation of the shaft, reducing the risk of entanglement or injury.
5. Ventilation:
– If working in enclosed spaces or areas with poor ventilation, ensure adequate ventilation or use appropriate respiratory protective equipment to avoid inhalation of harmful fumes, gases, or dust particles.
6. Proper Lifting Techniques:
– When handling heavy cardan shafts or components, use proper lifting techniques to avoid strains or injuries. Employ lifting equipment, such as cranes or hoists, where necessary, and ensure the load capacity is not exceeded.
7. Inspection and Maintenance:
– Regularly inspect the condition of the cardan shaft, including universal joints, slip yokes, and other components. Look for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Perform routine maintenance and lubrication as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure safe and efficient operation.
8. Avoid Exceeding Design Limits:
– Operate the cardan shaft within its specified design limits, including torque capacity, speed, and misalignment angles. Exceeding these limits can lead to premature wear, mechanical failure, and safety hazards.
9. Proper Disposal of Used Parts and Lubricants:
– Dispose of used parts, lubricants, and other waste materials in accordance with local regulations and environmental best practices. Follow proper disposal procedures to prevent pollution and potential harm to the environment.
10. Emergency Response:
– Be familiar with emergency response procedures, including first aid, fire prevention, and evacuation plans. Maintain access to emergency contact information and necessary safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers, in the vicinity of the work area.
It is important to note that the above safety precautions serve as general guidelines. Always refer to specific safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer of the cardan shaft or equipment for any additional precautions or recommendations.
By following these safety precautions, individuals working with cardan shafts can minimize the risks associated with their operation and ensure a safe working environment.

What benefits do cardan shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Cardan shafts, also known as propeller shafts or drive shafts, offer numerous benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. Their versatile design and functionality make them an essential component in various applications. Here are the key benefits that cardan shafts provide for different types of vehicles and equipment:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
– Cardan shafts ensure efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and buses, cardan shafts transmit torque from the gearbox or transmission to the differential, enabling the wheels to rotate and propel the vehicle forward. In equipment and machinery, cardan shafts transfer rotational power from the power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components like pumps, conveyors, or generators. By efficiently transmitting power, cardan shafts contribute to the overall performance and productivity of vehicles and equipment.
2. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts offer flexibility and the ability to compensate for misalignment between the driving and driven components. This flexibility is crucial in vehicles and equipment where the engine or power source may not be directly aligned with the wheels or driven machinery. Cardan shafts incorporate universal joints at each end, allowing for angular misalignment and accommodating variations in the relative positions of the components. This feature ensures smooth power transmission, reduces stress on the drivetrain, and enhances the overall maneuverability and performance of vehicles and equipment.
3. Adaptability to Variable Configurations:
– Cardan shafts are adaptable to variable configurations and adjustable setups. In vehicles, they can accommodate changes in the wheelbase or suspension system, allowing for different vehicle sizes and configurations. For example, in trucks with multiple axles, cardan shafts can be adjusted to compensate for varying distances between the axles. In equipment and machinery, cardan shafts can be designed with telescopic sections or sliding splines, enabling length adjustment to accommodate changes in the distance between the power source and driven components. This adaptability makes cardan shafts suitable for a wide range of vehicle and equipment configurations.
4. Vibration Damping and Smooth Operation:
– Cardan shafts contribute to vibration damping and enable smooth operation in vehicles and equipment. The universal joints in cardan shafts help absorb and dampen vibrations that may arise from the power source or drivetrain. By allowing slight angular deflection and compensating for misalignment, cardan shafts reduce the transmission of vibrations to the vehicle or equipment, resulting in a smoother and more comfortable ride for passengers or operators. Additionally, the balanced design of cardan shafts minimizes vibration-induced wear and extends the lifespan of associated components.
5. Safety and Protection:
– Cardan shafts incorporate safety features to ensure the protection of both the vehicle or equipment and the operator. For example, in vehicles, cardan shafts often have shielding or guards to prevent contact with rotating components, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. In some applications, cardan shafts may also include safety mechanisms such as shear pins or torque limiters. These features are designed to protect the shaft and other components from damage by shearing or disengaging in the event of overload or excessive torque, preventing costly repairs and downtime.
6. Suitable for Various Applications:
– Cardan shafts find applications in a wide range of vehicles and equipment across different industries. In the automotive sector, they are used in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, buses, and off-road vehicles to transmit power to the wheels. In the agricultural industry, cardan shafts connect tractors to various implements, such as mowers, balers, or tillers. In the construction and mining sectors, they are employed in machinery like excavators, loaders, and crushers to transfer power to different components. The versatility of cardan shafts makes them well-suited for various applications, providing reliable power transmission and motion.
In summary, cardan shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They ensure efficient power transmission, flexibility, and misalignment compensation, adaptability to variable configurations, vibration damping, and smooth operation. Additionally, they incorporate safety features and are suitable for a wide range of applications in automotive, agricultural, construction, and other industries. Cardan shafts play a vital role in enhancing the performance, maneuverability, and safety of vehicles and equipment, contributing to overall productivity and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-01-19
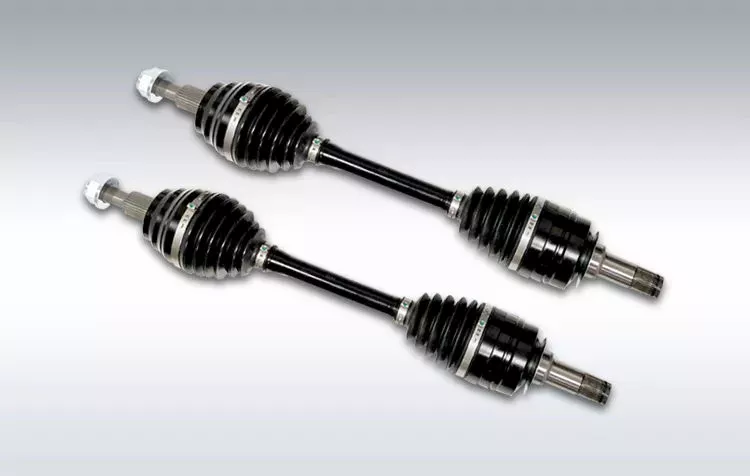
China wholesaler Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What factors should be considered when selecting the right cardan shaft for an application?
When selecting a cardan shaft for a specific application, several crucial factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The following factors should be taken into account during the selection process:
1. Torque Requirements:
– One of the primary considerations is the torque requirements of the application. The cardan shaft should be capable of transmitting the required torque without exceeding its rated capacity. It is essential to determine the maximum torque that the shaft will experience during operation and select a cardan shaft that can handle that torque while providing an appropriate safety margin.
2. Speed and RPM:
– The rotational speed or RPM (revolutions per minute) of the application is another critical factor. Cardan shafts have specific rotational speed limits, and exceeding these limits can lead to premature wear, vibration, and failure. It is crucial to select a cardan shaft that is rated for the speed requirements of the application to ensure reliable and smooth operation.
3. Angle of Misalignment:
– The angle of misalignment between the driving and driven components should be considered. Cardan shafts can accommodate angular misalignment up to a certain degree, typically specified by the manufacturer. It is important to select a cardan shaft that can handle the anticipated misalignment angle to ensure proper power transmission and prevent excessive wear or binding.
4. Operating Conditions:
– The operating conditions of the application play a vital role in cardan shaft selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, presence of corrosive agents, and exposure to vibration or shock need to be considered. It is crucial to select a cardan shaft that is designed to withstand the specific operating conditions to ensure durability and reliability.
5. Length and Size:
– The length and size of the cardan shaft should be chosen appropriately for the application. The length of the shaft affects its ability to absorb vibrations and accommodate misalignments. It is important to consider the available space and the required length to ensure proper fitment and functionality. Additionally, the size of the cardan shaft should be selected based on the load requirements and the available torque capacity.
6. Maintenance and Serviceability:
– Consideration should be given to the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the cardan shaft. Some applications may require regular inspection, lubrication, or replacement of certain components. It is beneficial to select a cardan shaft that allows convenient access for maintenance and incorporates features such as grease fittings or easily replaceable universal joints.
7. Cost and Budget:
– Finally, the cost and budget constraints should be taken into account. Different cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers may offer varying prices for their products. It is important to balance the desired quality, performance, and durability of the cardan shaft with the available budget.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers and designers can select the right cardan shaft for the application, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and reliability. Collaboration with cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers can also provide valuable insights and assistance in making the appropriate selection based on the specific requirements of the application.

How do cardan shafts handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment during operation?
Cardan shafts are designed to handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment during operation. They incorporate specific features and mechanisms to accommodate these factors and ensure efficient power transmission. Let’s explore how cardan shafts handle these variations:
1. Load Variation:
– Cardan shafts are designed to transmit torque and handle variations in load. The torque capacity of the shaft is determined based on the application’s requirements, and the shaft is manufactured using materials and dimensions that can withstand the specified loads. The design and construction of the shaft, including the selection of universal joints and slip yokes, are optimized to handle the anticipated loads. By choosing appropriate material strengths and dimensions, cardan shafts can effectively transmit varying loads without failure or excessive deflection.
2. Speed Variation:
– Cardan shafts can accommodate variations in rotational speed between the driving and driven components. The universal joints, which connect the shaft’s segments, allow for angular movement, thereby compensating for speed differences. The design of the universal joints and the use of needle bearings or roller bearings enable smooth rotation and efficient power transmission even at varying speeds. However, it’s important to note that excessively high speeds can introduce additional challenges such as increased vibration and wear, which may require additional measures such as balancing and lubrication.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts are specifically designed to handle misalignment between the driving and driven components. They can accommodate angular misalignment, parallel offset, and axial displacement to a certain extent. The universal joints in the shaft assembly allow for flexibility and articulation, enabling the shaft to transmit torque even when the components are not perfectly aligned. The design of the universal joints, along with their bearing arrangements and seals, allows for smooth rotation and compensation of misalignment. Manufacturers specify the maximum allowable misalignment angles and displacements for cardan shafts, and exceeding these limits can lead to increased wear, vibration, and reduced efficiency.
4. Telescopic Design:
– Cardan shafts often feature a telescopic design, which allows for axial movement and adjustment to accommodate variations in distance between the driving and driven components. This telescopic design enables the shaft to handle changes in length during operation, such as when the vehicle or equipment undergoes suspension movement or when the drivetrain components experience positional changes. The telescopic mechanism ensures that the shaft remains properly connected and engaged, maintaining power transmission efficiency even when there are fluctuations in distance or position.
5. Regular Maintenance:
– To ensure optimal performance and longevity, cardan shafts require regular maintenance. This includes inspections, lubrication of universal joints and slip yokes, and monitoring for wear or damage. Regular maintenance helps identify and address any issues related to load, speed, or misalignment variations, ensuring that the shaft continues to function effectively under changing operating conditions.
Overall, cardan shafts handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment through their design features such as universal joints, telescopic design, and flexibility. By incorporating these elements, along with proper material selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices, cardan shafts can reliably transmit torque and accommodate the changing operating conditions in vehicles and equipment.
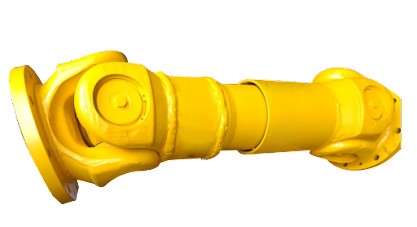
Can you explain the components and structure of a cardan shaft system?
A cardan shaft system, also known as a propeller shaft or drive shaft, consists of several components that work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components. The structure of a cardan shaft system typically includes the following components:
1. Shaft Tubes:
– The shaft tubes are the main structural elements of a cardan shaft system. They are cylindrical tubes made of durable and high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum alloy. The shaft tubes provide the backbone of the system and are responsible for transmitting torque and rotational power. They are designed to withstand high loads and torsional forces without deformation or failure.
2. Universal Joints:
– Universal joints, also known as U-joints or Cardan joints, are crucial components of a cardan shaft system. They are used to connect and articulate the shaft tubes, allowing for angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Universal joints consist of a cross-shaped yoke with needle bearings at each end. The yoke connects the shaft tubes, while the needle bearings enable the rotational motion and flexibility required for misalignment compensation. Universal joints allow the cardan shaft system to transmit torque even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned.
3. Slip Yokes:
– Slip yokes are components used in cardan shaft systems that can accommodate axial misalignment. They are typically located at one or both ends of the shaft tubes and provide a sliding connection between the shaft and the driving or driven component. Slip yokes allow the shaft to adjust its length and compensate for changes in the distance between the components. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the distance between the driving and driven components can vary, such as vehicles with adjustable wheelbases or machinery with variable attachment points.
4. Flanges and Yokes:
– Flanges and yokes are used to connect the cardan shaft system to the driving and driven components. Flanges are typically bolted or welded to the ends of the shaft tubes and provide a secure connection point. They have a flange face with bolt holes that align with the corresponding flange on the driving or driven component. Yokes, on the other hand, are cross-shaped components that connect the universal joints to the flanges. They have holes or grooves that accommodate the needle bearings of the universal joints, allowing for rotational motion and torque transfer.
5. Balancing Weights:
– Balancing weights are used to balance the cardan shaft system and minimize vibrations. As the shaft rotates, imbalances in the mass distribution can lead to vibrations, noise, and reduced performance. Balancing weights are strategically placed along the shaft tubes to counterbalance these imbalances. They redistribute the mass, ensuring that the rotational components of the cardan shaft system are properly balanced. Proper balancing improves stability, reduces wear on bearings and other components, and enhances the overall performance and lifespan of the shaft system.
6. Safety Features:
– Some cardan shaft systems incorporate safety features to protect against mechanical failures. For example, protective guards or shielding may be installed to prevent contact with rotating components, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. In applications where excessive forces or torques can occur, cardan shaft systems may include safety mechanisms such as shear pins or torque limiters. These features are designed to protect the shaft and other components from damage by shearing or disengaging in case of overload or excessive torque.
In summary, a cardan shaft system consists of shaft tubes, universal joints, slip yokes, flanges, and yokes, as well as balancing weights and safety features. These components work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components, allowing for angular and axial misalignment compensation. The structure and components of a cardan shaft system are carefully designed to ensure efficient power transmission, flexibility, durability, and safety in various applications.


editor by CX 2024-01-18
China supplier Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can cardan shafts be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Yes, cardan shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. They are versatile components that offer efficient power transmission and can be customized to meet the specific requirements of various applications. Let’s explore how cardan shafts can be adapted for both automotive and industrial settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
– Cardan shafts have long been used in automotive applications, especially in vehicles with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive systems. They are commonly found in cars, trucks, SUVs, and commercial vehicles. In the automotive sector, cardan shafts are primarily used to transmit torque from the engine or transmission to the differential or axle, allowing power to be distributed to the wheels. They provide a reliable and efficient means of transferring power, even in vehicles that experience varying loads, vibration, and misalignment. Cardan shafts in automotive applications are typically designed to handle specific torque and speed requirements, taking into account factors such as vehicle weight, horsepower, and intended use.
2. Industrial Applications:
– Cardan shafts are also widely used in various industrial settings where torque needs to be transmitted between two rotating components. They are employed in a diverse range of industries, including manufacturing, mining, agriculture, construction, and more. In industrial applications, cardan shafts are utilized in machinery, equipment, and systems that require efficient power transmission over long distances or in situations where angular misalignment is present. Industrial cardan shafts can be customized to accommodate specific torque, speed, and misalignment requirements, considering factors such as the load, rotational speed, operating conditions, and space constraints. They are commonly used in applications such as conveyors, pumps, generators, mixers, crushers, and other industrial machinery.
3. Customization and Adaptability:
– Cardan shafts can be adapted for various automotive and industrial applications through customization. Manufacturers offer a range of cardan shaft options with different lengths, sizes, torque capacities, and speed ratings to suit specific requirements. Universal joints, slip yokes, telescopic sections, and other components can be selected or designed to meet the demands of different settings. Additionally, cardan shafts can be made from different materials, such as steel or aluminum alloy, depending on the application’s needs for strength, durability, or weight reduction. By collaborating with cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers, automotive and industrial engineers can adapt these components to their specific settings, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
4. Consideration of Application-Specific Factors:
– When adapting cardan shafts for automotive or industrial settings, it is crucial to consider application-specific factors. These factors may include torque requirements, speed limits, operating conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.), space limitations, and the need for maintenance and serviceability. By carefully evaluating these factors and collaborating with experts, engineers can select or design cardan shafts that meet the unique demands of the automotive or industrial application.
In summary, cardan shafts can be adapted and customized for use in both automotive and industrial settings. Their versatility, efficient power transmission capabilities, and ability to accommodate misalignment make them suitable for a wide range of applications. By considering the specific requirements and collaborating with cardan shaft manufacturers, engineers can ensure that these components provide reliable and efficient power transfer in automotive and industrial systems.

How do cardan shafts handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment during operation?
Cardan shafts are designed to handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment during operation. They incorporate specific features and mechanisms to accommodate these factors and ensure efficient power transmission. Let’s explore how cardan shafts handle these variations:
1. Load Variation:
– Cardan shafts are designed to transmit torque and handle variations in load. The torque capacity of the shaft is determined based on the application’s requirements, and the shaft is manufactured using materials and dimensions that can withstand the specified loads. The design and construction of the shaft, including the selection of universal joints and slip yokes, are optimized to handle the anticipated loads. By choosing appropriate material strengths and dimensions, cardan shafts can effectively transmit varying loads without failure or excessive deflection.
2. Speed Variation:
– Cardan shafts can accommodate variations in rotational speed between the driving and driven components. The universal joints, which connect the shaft’s segments, allow for angular movement, thereby compensating for speed differences. The design of the universal joints and the use of needle bearings or roller bearings enable smooth rotation and efficient power transmission even at varying speeds. However, it’s important to note that excessively high speeds can introduce additional challenges such as increased vibration and wear, which may require additional measures such as balancing and lubrication.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts are specifically designed to handle misalignment between the driving and driven components. They can accommodate angular misalignment, parallel offset, and axial displacement to a certain extent. The universal joints in the shaft assembly allow for flexibility and articulation, enabling the shaft to transmit torque even when the components are not perfectly aligned. The design of the universal joints, along with their bearing arrangements and seals, allows for smooth rotation and compensation of misalignment. Manufacturers specify the maximum allowable misalignment angles and displacements for cardan shafts, and exceeding these limits can lead to increased wear, vibration, and reduced efficiency.
4. Telescopic Design:
– Cardan shafts often feature a telescopic design, which allows for axial movement and adjustment to accommodate variations in distance between the driving and driven components. This telescopic design enables the shaft to handle changes in length during operation, such as when the vehicle or equipment undergoes suspension movement or when the drivetrain components experience positional changes. The telescopic mechanism ensures that the shaft remains properly connected and engaged, maintaining power transmission efficiency even when there are fluctuations in distance or position.
5. Regular Maintenance:
– To ensure optimal performance and longevity, cardan shafts require regular maintenance. This includes inspections, lubrication of universal joints and slip yokes, and monitoring for wear or damage. Regular maintenance helps identify and address any issues related to load, speed, or misalignment variations, ensuring that the shaft continues to function effectively under changing operating conditions.
Overall, cardan shafts handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment through their design features such as universal joints, telescopic design, and flexibility. By incorporating these elements, along with proper material selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices, cardan shafts can reliably transmit torque and accommodate the changing operating conditions in vehicles and equipment.

Which industries and vehicles commonly use cardan shafts for power distribution?
Cardan shafts, also known as propeller shafts or drive shafts, are widely used in various industries and vehicles for efficient power distribution. Their versatility and ability to transmit torque between non-aligned components make them essential in numerous applications. Here are some of the industries and vehicles that commonly utilize cardan shafts:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Cardan shafts have extensive use in the automotive industry. They are found in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles. In these vehicles, cardan shafts transmit torque from the gearbox or transmission to the differential, which then distributes the power to the wheels. This allows the wheels to rotate and propel the vehicle forward. Cardan shafts in the automotive industry are designed to handle high torque loads and provide smooth power delivery, contributing to the overall performance and drivability of the vehicles.
2. Agriculture and Farming:
– The agriculture and farming sector extensively relies on cardan shafts for power distribution. They are commonly used in tractors and other agricultural machinery to transfer power from the engine to various implements and attachments, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. Cardan shafts in agricultural applications enable efficient power delivery to the implements, allowing farmers to perform tasks like cutting crops, baling hay, tilling soil, and harvesting with ease and productivity.
3. Construction and Mining:
– The construction and mining industries utilize cardan shafts in a wide range of machinery and equipment. Excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and crushers are examples of machinery that employ cardan shafts to transmit power to different components. In these applications, cardan shafts ensure efficient power distribution from the engine or motor to the drivetrain or specific attachments, enabling the machinery to perform tasks like digging, material handling, and crushing with the required power and precision.
4. Industrial Equipment and Machinery:
– Various industrial equipment and machinery rely on cardan shafts for power transmission. They are used in pumps, compressors, generators, conveyors, mixers, and other industrial machines. Cardan shafts in industrial applications transmit rotational power from the motor or engine to the driven components, enabling the machinery to perform their specific functions. The flexibility and misalignment compensation provided by cardan shafts are particularly valuable in industrial settings where the power source and driven components may not be perfectly aligned.
5. Marine and Shipbuilding:
– The marine and shipbuilding industry also utilizes cardan shafts for power distribution. They are commonly found in propulsion systems of boats and ships. Cardan shafts in marine applications connect the engine or motor to the propeller, ensuring efficient transmission of rotational power and enabling the vessel to navigate through water. The ability of cardan shafts to compensate for misalignment and accommodate variations in the shaft angle is crucial in marine applications, where the propeller shaft may not be in a direct alignment with the engine.
6. Rail and Locomotives:
– Rail and locomotive systems employ cardan shafts for power distribution. They are crucial components in the drivetrain of locomotives and trains, enabling the transmission of torque from the engine or motor to the wheels or axles. Cardan shafts in rail applications ensure efficient power delivery, allowing locomotives and trains to transport passengers and goods with the required speed and traction.
In summary, cardan shafts are widely used in various industries and vehicles for power distribution. They are commonly found in the automotive industry, agriculture and farming, construction and mining machinery, industrial equipment, marine and shipbuilding applications, as well as rail and locomotive systems. The versatility, flexibility, and efficient power transmission provided by cardan shafts make them indispensable components in these industries and vehicles, contributing to their performance, productivity, and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-01-10
China Professional Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What factors should be considered when selecting the right cardan shaft for an application?
When selecting a cardan shaft for a specific application, several crucial factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The following factors should be taken into account during the selection process:
1. Torque Requirements:
– One of the primary considerations is the torque requirements of the application. The cardan shaft should be capable of transmitting the required torque without exceeding its rated capacity. It is essential to determine the maximum torque that the shaft will experience during operation and select a cardan shaft that can handle that torque while providing an appropriate safety margin.
2. Speed and RPM:
– The rotational speed or RPM (revolutions per minute) of the application is another critical factor. Cardan shafts have specific rotational speed limits, and exceeding these limits can lead to premature wear, vibration, and failure. It is crucial to select a cardan shaft that is rated for the speed requirements of the application to ensure reliable and smooth operation.
3. Angle of Misalignment:
– The angle of misalignment between the driving and driven components should be considered. Cardan shafts can accommodate angular misalignment up to a certain degree, typically specified by the manufacturer. It is important to select a cardan shaft that can handle the anticipated misalignment angle to ensure proper power transmission and prevent excessive wear or binding.
4. Operating Conditions:
– The operating conditions of the application play a vital role in cardan shaft selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, presence of corrosive agents, and exposure to vibration or shock need to be considered. It is crucial to select a cardan shaft that is designed to withstand the specific operating conditions to ensure durability and reliability.
5. Length and Size:
– The length and size of the cardan shaft should be chosen appropriately for the application. The length of the shaft affects its ability to absorb vibrations and accommodate misalignments. It is important to consider the available space and the required length to ensure proper fitment and functionality. Additionally, the size of the cardan shaft should be selected based on the load requirements and the available torque capacity.
6. Maintenance and Serviceability:
– Consideration should be given to the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the cardan shaft. Some applications may require regular inspection, lubrication, or replacement of certain components. It is beneficial to select a cardan shaft that allows convenient access for maintenance and incorporates features such as grease fittings or easily replaceable universal joints.
7. Cost and Budget:
– Finally, the cost and budget constraints should be taken into account. Different cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers may offer varying prices for their products. It is important to balance the desired quality, performance, and durability of the cardan shaft with the available budget.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers and designers can select the right cardan shaft for the application, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and reliability. Collaboration with cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers can also provide valuable insights and assistance in making the appropriate selection based on the specific requirements of the application.

How do cardan shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution?
Cardan shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution. They enable the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing for effective power transmission and optimized performance. Here’s how cardan shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution:
1. Torque Transmission:
– Cardan shafts are responsible for transmitting torque from the engine or power source to the wheels. By efficiently transferring rotational force, they enable propulsion and movement of the vehicle. The design and construction of the cardan shaft ensure minimal power loss during torque transmission, contributing to the overall efficiency of the propulsion system.
2. Power Distribution:
– In vehicles with multiple axles or wheels, cardan shafts distribute power to each axle or wheel, ensuring balanced power delivery. This allows for improved traction, stability, and control, especially in situations such as acceleration, cornering, or off-road driving. By evenly distributing power, cardan shafts optimize the utilization of the available engine power and contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
3. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts offer flexibility and the ability to accommodate misalignment between the engine, drivetrain, and wheels. They can handle angular misalignment, parallel offset, and axial displacement, allowing for smooth power transmission even when the components are not perfectly aligned. This flexibility helps reduce mechanical stresses and energy losses caused by misalignment, thus improving the efficiency of power transfer.
4. Vibration Damping:
– Cardan shafts can help dampen vibrations transmitted from the engine or other drivetrain components. The universal joints in the shaft assembly allow for slight angular movement, which helps absorb and dampen vibrations generated during operation. By reducing vibrations, cardan shafts contribute to a smoother and more efficient power distribution, enhancing overall vehicle performance and comfort.
5. Weight Reduction:
– Cardan shafts, when compared to alternative drivetrain systems such as chain or belt drives, can contribute to weight reduction in vehicles. The use of lightweight materials and optimized designs helps reduce the overall weight of the propulsion system. Reduced weight improves fuel efficiency, as less energy is required to propel the vehicle. Cardan shafts’ compactness and space-saving design also allow for more efficient packaging of the drivetrain components.
6. Durability and Reliability:
– Cardan shafts are designed to withstand the demands of vehicle propulsion and power distribution over extended periods. They are engineered using durable materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and longevity. By providing a robust and dependable power transmission solution, cardan shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the propulsion system by minimizing downtime and maintenance requirements.
Overall, cardan shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution by effectively transmitting torque, balancing power distribution, compensating for misalignment, dampening vibrations, reducing weight, and ensuring durability and reliability. Their role in optimizing power transfer and enhancing overall vehicle performance makes cardan shafts an integral component of efficient propulsion systems.

What benefits do cardan shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Cardan shafts, also known as propeller shafts or drive shafts, offer numerous benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. Their versatile design and functionality make them an essential component in various applications. Here are the key benefits that cardan shafts provide for different types of vehicles and equipment:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
– Cardan shafts ensure efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and buses, cardan shafts transmit torque from the gearbox or transmission to the differential, enabling the wheels to rotate and propel the vehicle forward. In equipment and machinery, cardan shafts transfer rotational power from the power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components like pumps, conveyors, or generators. By efficiently transmitting power, cardan shafts contribute to the overall performance and productivity of vehicles and equipment.
2. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts offer flexibility and the ability to compensate for misalignment between the driving and driven components. This flexibility is crucial in vehicles and equipment where the engine or power source may not be directly aligned with the wheels or driven machinery. Cardan shafts incorporate universal joints at each end, allowing for angular misalignment and accommodating variations in the relative positions of the components. This feature ensures smooth power transmission, reduces stress on the drivetrain, and enhances the overall maneuverability and performance of vehicles and equipment.
3. Adaptability to Variable Configurations:
– Cardan shafts are adaptable to variable configurations and adjustable setups. In vehicles, they can accommodate changes in the wheelbase or suspension system, allowing for different vehicle sizes and configurations. For example, in trucks with multiple axles, cardan shafts can be adjusted to compensate for varying distances between the axles. In equipment and machinery, cardan shafts can be designed with telescopic sections or sliding splines, enabling length adjustment to accommodate changes in the distance between the power source and driven components. This adaptability makes cardan shafts suitable for a wide range of vehicle and equipment configurations.
4. Vibration Damping and Smooth Operation:
– Cardan shafts contribute to vibration damping and enable smooth operation in vehicles and equipment. The universal joints in cardan shafts help absorb and dampen vibrations that may arise from the power source or drivetrain. By allowing slight angular deflection and compensating for misalignment, cardan shafts reduce the transmission of vibrations to the vehicle or equipment, resulting in a smoother and more comfortable ride for passengers or operators. Additionally, the balanced design of cardan shafts minimizes vibration-induced wear and extends the lifespan of associated components.
5. Safety and Protection:
– Cardan shafts incorporate safety features to ensure the protection of both the vehicle or equipment and the operator. For example, in vehicles, cardan shafts often have shielding or guards to prevent contact with rotating components, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. In some applications, cardan shafts may also include safety mechanisms such as shear pins or torque limiters. These features are designed to protect the shaft and other components from damage by shearing or disengaging in the event of overload or excessive torque, preventing costly repairs and downtime.
6. Suitable for Various Applications:
– Cardan shafts find applications in a wide range of vehicles and equipment across different industries. In the automotive sector, they are used in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, buses, and off-road vehicles to transmit power to the wheels. In the agricultural industry, cardan shafts connect tractors to various implements, such as mowers, balers, or tillers. In the construction and mining sectors, they are employed in machinery like excavators, loaders, and crushers to transfer power to different components. The versatility of cardan shafts makes them well-suited for various applications, providing reliable power transmission and motion.
In summary, cardan shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They ensure efficient power transmission, flexibility, and misalignment compensation, adaptability to variable configurations, vibration damping, and smooth operation. Additionally, they incorporate safety features and are suitable for a wide range of applications in automotive, agricultural, construction, and other industries. Cardan shafts play a vital role in enhancing the performance, maneuverability, and safety of vehicles and equipment, contributing to overall productivity and reliability.


editor by CX 2023-12-15
China Good quality Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How do cardan shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Cardan shafts are designed to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance between the driving and driven components. They employ various mechanisms and features that contribute to both aspects. Let’s explore how cardan shafts achieve efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Universal Joints:
– Cardan shafts utilize universal joints, also known as U-joints, to transmit torque from the driving component to the driven component. Universal joints consist of a cross-shaped yoke with needle bearings at each end. These needle bearings allow the joints to pivot and accommodate angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. By allowing for flexibility in movement, universal joints ensure efficient power transfer even when the components are not perfectly aligned, minimizing energy losses and maintaining balance.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts are designed to compensate for misalignment between the driving and driven components. The universal joints, along with slip yokes and telescopic sections, allow the shaft to adjust its length and accommodate variations in alignment. This misalignment compensation capability ensures that the cardan shaft can transmit power smoothly and efficiently, reducing stress on the components and maintaining balance during operation.
3. Balanced Design:
– Cardan shafts are engineered with a balanced design to minimize vibration and maintain smooth operation. The shaft tubes are typically symmetrically constructed, and the universal joints are positioned to distribute the mass evenly. This balanced design helps to reduce vibration and minimize the occurrence of unbalanced forces that can negatively impact power transfer and overall system performance. By maintaining balance, cardan shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improve the lifespan of the components involved.
4. High-Quality Materials and Manufacturing:
– The materials used in the construction of cardan shafts, such as steel or aluminum alloy, are carefully selected for their strength, durability, and ability to maintain balance. High-quality materials ensure that the shafts can withstand the torque and operational stresses without deformation or failure, promoting efficient power transfer. Additionally, precise manufacturing processes and quality control measures are employed to ensure that the cardan shafts are accurately balanced during production, further enhancing their efficiency and balance.
5. Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
– To ensure continued efficient power transfer and balance, regular maintenance and inspection of cardan shafts are essential. This includes periodic lubrication of the universal joints, checking for wear or damage, and addressing any misalignment issues. Regular maintenance helps to preserve the balance of the shaft and ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Overall, cardan shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through the use of universal joints for torque transmission, misalignment compensation mechanisms, balanced design, high-quality materials, and regular maintenance. By incorporating these features, cardan shafts contribute to the smooth operation, reliability, and longevity of various applications in automotive, industrial, and other sectors that rely on efficient power transmission.

How do cardan shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution?
Cardan shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution. They enable the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing for effective power transmission and optimized performance. Here’s how cardan shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution:
1. Torque Transmission:
– Cardan shafts are responsible for transmitting torque from the engine or power source to the wheels. By efficiently transferring rotational force, they enable propulsion and movement of the vehicle. The design and construction of the cardan shaft ensure minimal power loss during torque transmission, contributing to the overall efficiency of the propulsion system.
2. Power Distribution:
– In vehicles with multiple axles or wheels, cardan shafts distribute power to each axle or wheel, ensuring balanced power delivery. This allows for improved traction, stability, and control, especially in situations such as acceleration, cornering, or off-road driving. By evenly distributing power, cardan shafts optimize the utilization of the available engine power and contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
3. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts offer flexibility and the ability to accommodate misalignment between the engine, drivetrain, and wheels. They can handle angular misalignment, parallel offset, and axial displacement, allowing for smooth power transmission even when the components are not perfectly aligned. This flexibility helps reduce mechanical stresses and energy losses caused by misalignment, thus improving the efficiency of power transfer.
4. Vibration Damping:
– Cardan shafts can help dampen vibrations transmitted from the engine or other drivetrain components. The universal joints in the shaft assembly allow for slight angular movement, which helps absorb and dampen vibrations generated during operation. By reducing vibrations, cardan shafts contribute to a smoother and more efficient power distribution, enhancing overall vehicle performance and comfort.
5. Weight Reduction:
– Cardan shafts, when compared to alternative drivetrain systems such as chain or belt drives, can contribute to weight reduction in vehicles. The use of lightweight materials and optimized designs helps reduce the overall weight of the propulsion system. Reduced weight improves fuel efficiency, as less energy is required to propel the vehicle. Cardan shafts’ compactness and space-saving design also allow for more efficient packaging of the drivetrain components.
6. Durability and Reliability:
– Cardan shafts are designed to withstand the demands of vehicle propulsion and power distribution over extended periods. They are engineered using durable materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and longevity. By providing a robust and dependable power transmission solution, cardan shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the propulsion system by minimizing downtime and maintenance requirements.
Overall, cardan shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power distribution by effectively transmitting torque, balancing power distribution, compensating for misalignment, dampening vibrations, reducing weight, and ensuring durability and reliability. Their role in optimizing power transfer and enhancing overall vehicle performance makes cardan shafts an integral component of efficient propulsion systems.

Can you explain the components and structure of a cardan shaft system?
A cardan shaft system, also known as a propeller shaft or drive shaft, consists of several components that work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components. The structure of a cardan shaft system typically includes the following components:
1. Shaft Tubes:
– The shaft tubes are the main structural elements of a cardan shaft system. They are cylindrical tubes made of durable and high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum alloy. The shaft tubes provide the backbone of the system and are responsible for transmitting torque and rotational power. They are designed to withstand high loads and torsional forces without deformation or failure.
2. Universal Joints:
– Universal joints, also known as U-joints or Cardan joints, are crucial components of a cardan shaft system. They are used to connect and articulate the shaft tubes, allowing for angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Universal joints consist of a cross-shaped yoke with needle bearings at each end. The yoke connects the shaft tubes, while the needle bearings enable the rotational motion and flexibility required for misalignment compensation. Universal joints allow the cardan shaft system to transmit torque even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned.
3. Slip Yokes:
– Slip yokes are components used in cardan shaft systems that can accommodate axial misalignment. They are typically located at one or both ends of the shaft tubes and provide a sliding connection between the shaft and the driving or driven component. Slip yokes allow the shaft to adjust its length and compensate for changes in the distance between the components. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the distance between the driving and driven components can vary, such as vehicles with adjustable wheelbases or machinery with variable attachment points.
4. Flanges and Yokes:
– Flanges and yokes are used to connect the cardan shaft system to the driving and driven components. Flanges are typically bolted or welded to the ends of the shaft tubes and provide a secure connection point. They have a flange face with bolt holes that align with the corresponding flange on the driving or driven component. Yokes, on the other hand, are cross-shaped components that connect the universal joints to the flanges. They have holes or grooves that accommodate the needle bearings of the universal joints, allowing for rotational motion and torque transfer.
5. Balancing Weights:
– Balancing weights are used to balance the cardan shaft system and minimize vibrations. As the shaft rotates, imbalances in the mass distribution can lead to vibrations, noise, and reduced performance. Balancing weights are strategically placed along the shaft tubes to counterbalance these imbalances. They redistribute the mass, ensuring that the rotational components of the cardan shaft system are properly balanced. Proper balancing improves stability, reduces wear on bearings and other components, and enhances the overall performance and lifespan of the shaft system.
6. Safety Features:
– Some cardan shaft systems incorporate safety features to protect against mechanical failures. For example, protective guards or shielding may be installed to prevent contact with rotating components, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. In applications where excessive forces or torques can occur, cardan shaft systems may include safety mechanisms such as shear pins or torque limiters. These features are designed to protect the shaft and other components from damage by shearing or disengaging in case of overload or excessive torque.
In summary, a cardan shaft system consists of shaft tubes, universal joints, slip yokes, flanges, and yokes, as well as balancing weights and safety features. These components work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components, allowing for angular and axial misalignment compensation. The structure and components of a cardan shaft system are carefully designed to ensure efficient power transmission, flexibility, durability, and safety in various applications.


editor by CX 2023-12-08
China supplier Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2023-12-06
China Professional Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2023-12-06
China factory Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by CX 2023-12-04
China Custom Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of cardan shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers take several measures to ensure the compatibility of cardan shafts with different equipment. These measures involve careful design, engineering, and manufacturing processes to meet the specific requirements of diverse applications. Let’s explore how manufacturers ensure compatibility:
1. Application Analysis:
– Manufacturers begin by analyzing the application requirements and specifications provided by customers. This analysis includes understanding factors such as torque, speed, misalignment, operating conditions, space limitations, and other specific needs. By evaluating these parameters, manufacturers can determine the appropriate design and configuration of the cardan shaft to ensure compatibility with the equipment.
2. Customization Options:
– Manufacturers offer customization options for cardan shafts to meet the unique requirements of different equipment. This includes providing various lengths, sizes, torque capacities, connection methods, and material options. Customers can work closely with manufacturers to select or design a cardan shaft that fits their specific equipment and ensures compatibility with the system’s power transmission needs.
3. Engineering Expertise:
– Manufacturers employ experienced engineers who specialize in cardan shaft design and engineering. These experts have in-depth knowledge of mechanical power transmission and understand the complexities involved in ensuring compatibility. They use their expertise to design cardan shafts that can handle the specific torque, speed, misalignment, and other parameters required by different equipment.
4. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Simulation:
– Manufacturers utilize advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools to model and simulate the behavior of cardan shafts in different equipment scenarios. These tools allow engineers to analyze the stress distribution, bearing performance, and other critical factors to ensure the shaft’s compatibility and performance. By simulating the cardan shaft’s behavior under various loading conditions, manufacturers can optimize its design and validate its compatibility.
5. Quality Control and Testing:
– Manufacturers have stringent quality control processes in place to ensure the reliability, durability, and compatibility of cardan shafts. They conduct thorough testing to verify the performance and functionality of the shafts in real-world conditions. This may involve testing for torque capacity, speed limits, vibration resistance, misalignment tolerance, and other relevant parameters. By subjecting the cardan shafts to rigorous testing, manufacturers can ensure their compatibility with different equipment and validate their ability to deliver reliable power transmission.
6. Adherence to Standards and Regulations:
– Manufacturers follow industry standards and regulations when designing and manufacturing cardan shafts. Compliance with these standards ensures that the shafts meet the necessary safety, performance, and compatibility requirements. Examples of such standards include ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to producing compatible and high-quality cardan shafts.
7. Collaboration with Customers:
– Manufacturers actively collaborate with customers to understand their equipment and system requirements. They engage in discussions, provide technical support, and offer guidance to ensure the compatibility of the cardan shafts. By fostering a collaborative relationship, manufacturers can address specific challenges and tailor the design and specifications of the shaft to meet the unique requirements of different equipment.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of cardan shafts with different equipment through application analysis, customization options, engineering expertise, CAD and simulation tools, quality control and testing, adherence to standards, and collaboration with customers. These measures allow manufacturers to design and produce cardan shafts that meet the specific torque, speed, misalignment, and other requirements of various equipment, ensuring optimal compatibility and efficient power transmission.

How do cardan shafts enhance the performance of trucks and heavy-duty vehicles?
Cardan shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of trucks and heavy-duty vehicles. These vehicles often operate under demanding conditions, requiring robust and efficient power transmission systems. Here’s how cardan shafts contribute to the performance of trucks and heavy-duty vehicles:
1. Torque Transmission:
– Cardan shafts enable the efficient transmission of torque from the engine or transmission to the drivetrain and wheels of trucks and heavy-duty vehicles. They can handle high torque loads, ensuring that power is effectively transferred to propel the vehicle forward. This efficient torque transmission enhances acceleration, towing capacity, and overall performance.
2. Power Distribution:
– Trucks and heavy-duty vehicles often have multiple axles or wheels. Cardan shafts distribute power to each axle or wheel, ensuring balanced power delivery. This helps improve traction, stability, and control, especially when carrying heavy loads or operating on challenging terrains. By optimizing power distribution, cardan shafts enhance the vehicle’s performance and handling characteristics.
3. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts are designed to accommodate misalignment between the engine, transmission, and drivetrain components. They can handle angular misalignment, parallel offset, and axial displacement. This flexibility allows for smooth power transmission even when the components are not perfectly aligned, reducing stress on the drivetrain and improving performance. It also helps absorb vibrations and shocks, enhancing driver comfort and reducing wear on other vehicle components.
4. Durability and Reliability:
– Heavy-duty vehicles operate in rugged and demanding conditions, such as construction sites, mining operations, or long-haul transportation. Cardan shafts are built to withstand these harsh environments, providing durability and reliability. They are designed using robust materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can handle the high torque, heavy loads, and continuous operation that trucks and heavy-duty vehicles require. This reliability minimizes downtime and maintenance, improving overall vehicle performance.
5. Powertrain Efficiency:
– Cardan shafts help optimize powertrain efficiency in trucks and heavy-duty vehicles. By efficiently transmitting torque and minimizing power loss during power transfer, they contribute to improved fuel economy and reduced energy consumption. This increased efficiency translates to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
6. Weight Reduction:
– Cardan shafts offer weight reduction benefits for trucks and heavy-duty vehicles. The use of lightweight materials and optimized designs helps reduce the overall weight of the propulsion system. Reduced weight improves fuel efficiency, increases payload capacity, and enhances vehicle maneuverability. Cardan shafts’ compactness and space-saving design also allow for more efficient packaging of the drivetrain components.
7. Adaptability to Various Configurations:
– Trucks and heavy-duty vehicles come in different configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), front-wheel drive (FWD), or all-wheel drive (AWD). Cardan shafts can be tailored to suit these various drivetrain setups, providing the necessary torque transmission and power distribution for each configuration. This adaptability allows manufacturers to optimize vehicle performance based on specific application requirements.
Overall, cardan shafts enhance the performance of trucks and heavy-duty vehicles by enabling efficient torque transmission, balancing power distribution, compensating for misalignment, providing durability and reliability, optimizing powertrain efficiency, reducing weight, and adapting to various drivetrain configurations. Their role in improving acceleration, towing capacity, traction, and fuel economy contributes to the overall performance and success of these vehicles in demanding environments.

Can you explain the components and structure of a cardan shaft system?
A cardan shaft system, also known as a propeller shaft or drive shaft, consists of several components that work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components. The structure of a cardan shaft system typically includes the following components:
1. Shaft Tubes:
– The shaft tubes are the main structural elements of a cardan shaft system. They are cylindrical tubes made of durable and high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum alloy. The shaft tubes provide the backbone of the system and are responsible for transmitting torque and rotational power. They are designed to withstand high loads and torsional forces without deformation or failure.
2. Universal Joints:
– Universal joints, also known as U-joints or Cardan joints, are crucial components of a cardan shaft system. They are used to connect and articulate the shaft tubes, allowing for angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Universal joints consist of a cross-shaped yoke with needle bearings at each end. The yoke connects the shaft tubes, while the needle bearings enable the rotational motion and flexibility required for misalignment compensation. Universal joints allow the cardan shaft system to transmit torque even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned.
3. Slip Yokes:
– Slip yokes are components used in cardan shaft systems that can accommodate axial misalignment. They are typically located at one or both ends of the shaft tubes and provide a sliding connection between the shaft and the driving or driven component. Slip yokes allow the shaft to adjust its length and compensate for changes in the distance between the components. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the distance between the driving and driven components can vary, such as vehicles with adjustable wheelbases or machinery with variable attachment points.
4. Flanges and Yokes:
– Flanges and yokes are used to connect the cardan shaft system to the driving and driven components. Flanges are typically bolted or welded to the ends of the shaft tubes and provide a secure connection point. They have a flange face with bolt holes that align with the corresponding flange on the driving or driven component. Yokes, on the other hand, are cross-shaped components that connect the universal joints to the flanges. They have holes or grooves that accommodate the needle bearings of the universal joints, allowing for rotational motion and torque transfer.
5. Balancing Weights:
– Balancing weights are used to balance the cardan shaft system and minimize vibrations. As the shaft rotates, imbalances in the mass distribution can lead to vibrations, noise, and reduced performance. Balancing weights are strategically placed along the shaft tubes to counterbalance these imbalances. They redistribute the mass, ensuring that the rotational components of the cardan shaft system are properly balanced. Proper balancing improves stability, reduces wear on bearings and other components, and enhances the overall performance and lifespan of the shaft system.
6. Safety Features:
– Some cardan shaft systems incorporate safety features to protect against mechanical failures. For example, protective guards or shielding may be installed to prevent contact with rotating components, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. In applications where excessive forces or torques can occur, cardan shaft systems may include safety mechanisms such as shear pins or torque limiters. These features are designed to protect the shaft and other components from damage by shearing or disengaging in case of overload or excessive torque.
In summary, a cardan shaft system consists of shaft tubes, universal joints, slip yokes, flanges, and yokes, as well as balancing weights and safety features. These components work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components, allowing for angular and axial misalignment compensation. The structure and components of a cardan shaft system are carefully designed to ensure efficient power transmission, flexibility, durability, and safety in various applications.


editor by CX 2023-11-18
China 65-9450 Front Drive Shaft for Ford Explorer 1997-2001 65-9294 Prop Propeller Cardan Shaft manufacturer
Product Description
PROPELLER SHAFT company & supplier – CZPT is your greatest decision
|
Merchandise Name |
Front Prop Drive Shaft Assembly For CZPT Explorer 97-01, Mountaineer V8 5.0L Four wheel drive |
|
Element Quantity |
65-9450, sixty five-9294, F77A4A376CB, 936-325, XL2Z4A376BB |
|
Motor vehicle Fitment |
For CZPT EXPLORER 1997-2001 |
|
Compressed Length |
28.46″ |
|
MOQ |
1pc if we have them in stock |
|
Shipping and delivery time |
1-7 days for inventory products, twenty five times for manufacturing items |
|
Observe |
Have inventory in China and US! |
For FORD Propeller Shaft, we have more than a hundred products, these kinds of as:
|
OE NO. |
Software |
OE NO. |
Application |
|
sixty five-9152 |
For CZPT CZPT 1966-1970 |
7L3Z 4R602-J |
For CZPT F-one hundred fifty 2004-2008 |
|
65-9153 |
For CZPT CZPT 1966-1977 |
4L34-4K145-RE |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2004-2009 |
|
65-9148 |
For CZPT F-250 1977-1979 |
4L34-4K145-RA |
For CZPT Lobo 2004-2571 |
|
65-9170 |
For CZPT CZPT 1978 |
6F9Z4R602A |
For CZPT 5 Hundred 05-07 |
|
sixty five-9164 |
For CZPT CZPT 1979 |
5F9Z4R602AA |
For CZPT Freestyle 2005-2007 |
|
sixty five-9166 |
For CZPT CZPT 1979 |
6F924R602-A |
For CZPT Five Hundred 05-07 |
|
65-9161 |
For CZPT CZPT 1979 |
5F934K145AE |
For CZPT Freestyle 2005-2007 |
|
sixty five-9158 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 1979 |
936-812 |
For CZPT Mustang 2005-2008 |
|
65-9160 |
For CZPT CZPT 1980-1982 |
8L3Z4R602H |
For CZPT F-one hundred fifty 2006-2008 |
|
65-9832 |
For CZPT CZPT 1983-1984 |
936-807 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2006-2008 |
|
65-9830 |
For CZPT Ranger 1983-1985 |
8L3Z4R602B |
For CZPT LOBO 2006-2008 |
|
sixty five-9831 |
For CZPT Ranger 1983-1985 |
7L3Z4R602K |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2006-2008 |
|
sixty five-9821 |
For CZPT CZPT II 1984-1990 |
CN4C154K357AD |
For CZPT Transit 2006-2014 |
|
65-9822 |
For CZPT CZPT II 1984-1990 |
7T434K357AC |
For CZPT Edge 2007-2008 |
|
sixty five-9430 |
For CZPT CZPT 1985-1986 |
6L2Z4A376B |
For CZPT Expedition 2007-2009 |
|
sixty five-9423 |
For CZPT Ranger 1985-1988 |
7T4Z4R602A |
For CZPT Edge 2007-2013 |
|
65-9431 |
For CZPT CZPT 1985-1989 |
936-847 |
For CZPT TAURUS X 2008-2009 |
|
sixty five-9721 |
For CZPT F-350 1985-1994 |
8L8Z4R602C |
For CZPT Escape 2008-2012 |
|
sixty five-9416 |
For CZPT CZPT 1987-1989 |
936-892 |
For CZPT ESCAPE 2008-2012 |
|
65-9400 |
For CZPT CZPT 1987-1989 |
7E5Z4R602A |
For CZPT FUSION 2008-2012 |
|
65-9636 |
For CZPT Ranger 1988 |
8G1Z4R602A |
For CZPT Taurus 2008-2015 |
|
sixty five-9638 |
For CZPT Ranger 1988-1989 |
936-809 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2571-2011 |
|
sixty five-9823 |
For CZPT CZPT II 1989-1990 |
AL344K145KA |
For CZPT LOBO 2571-2011 |
|
sixty five-9739 |
For CZPT F-350 1989-1994 |
946-831 |
For CZPT F-150 2011-2014 |
|
sixty five-9667 |
For CZPT F-350 1989-1994 |
BL3V4602BD |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2011-2014 |
|
938-066 |
For CZPT F-250 1989-1997 |
8G1Z4R602B |
For CZPT Explorer 2011-2015 |
|
65-9664 |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1993 |
BC3Z4A376A |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Obligation eleven-16 |
|
sixty five-9665 |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1994 |
5L834K145BA |
For CZPT Escape 2013-2017 |
|
sixty five-9662 |
For CZPT RANGER 1990-1994 |
7C19-4K145-DB |
For CZPT Transit 2015-2016 |
|
65-9660 |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1996 |
7C19-4K145-BB |
For CZPT Transit |
|
sixty five-9663 |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1996 |
7C19-4K145-DB |
For CZPT Transit 2015-2016 |
|
sixty five-9443 |
For CZPT CZPT 1988-1996 |
5L834K145BA |
For CZPT Escape 2013-2017 |
|
65-9444 |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1996 |
AL3Z4A376D |
For CZPT Expedition 2007-2014 |
|
65-9661 |
For CZPT EXPLORER 1991-1994 |
5C3Z4A376G |
For CZPT F250 Tremendous Duty ninety nine-04 |
|
sixty five-9624 |
For CZPT Explorer 1995-1996 |
CV6Z4R602B |
For CZPT Escape 2013-2016 |
|
65-9447 |
For CZPT F-350 1995-1996 |
4641968AE |
For CZPT Escape 2013-2016 |
|
65-9449 |
For CZPT F-350 1995-1996 |
BL3Z4R602D |
For CZPT F150 2011-2012 |
|
65-9675 |
For CZPT Ranger 1995-1997 |
ZZR0-25-100 |
For CZPT Explorer Activity Trac 05 |
|
65-9672 |
For CZPT F-100 1996-1997 |
2L8Z4R602BA |
For CZPT Escape 2001-2007 |
|
sixty five-9453 |
For CZPT F-one hundred fifty 1997-1998 |
XL2Z-4A376-AA |
For CZPT Explorer Activity 2002-2003 |
|
65-9544 |
For CZPT F-150 2004 |
1L2Z4A376A |
For CZPT EXPLORER 2002-2571 |
|
sixty five-9545 |
For CZPT F-one hundred fifty 1999-2003 |
936-805 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2004 |
|
65-9441 |
For CZPT CZPT 1988-1993 |
8L3Z4R602E |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2004-2008 |
|
65-2001 |
For CZPT EXPEDITION 06-14 |
8L3Z4R602F |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2004-2008 |
|
65-9305 |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Obligation ninety nine-01 |
sixty five-9302 |
For CZPT Tour 2001-2005 |
|
sixty five-9112 |
For CZPT F-250 Super Obligation ninety nine-02 |
E9TZ4A376B |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1996 |
|
65-9115 |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Obligation ninety nine-02 |
F6TZ4A376RA |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 1990-1996 |
|
938-304 |
For CZPT F-350 Tremendous Obligation 11-sixteen |
F77A4376BB |
For CZPT EXPLORER 1997-2001 |
|
936-802 |
For CZPT F-150 2004-2008 |
F75Z4A376BB |
For CZPT Expedition 1997-2002 |
|
65-9546 |
For CZPT Tour 2001-2005 |
F77Z4A376CB |
For CZPT EXPLORER 1998-2001 |
|
946-448 |
For CZPT F-350 Tremendous Duty 02-03 |
5L544602DB |
For CZPT Ranger 1998-2011 |
|
65-9304 |
For CZPT Excursion 2000-2003 |
5C3Z4A376D |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Obligation 99-06 |
|
sixty five-9303 |
For CZPT Excursion 2000-2003 |
YC3Z4A376EA |
For CZPT F-350 Tremendous Obligation ninety nine-06 |
|
938-082 |
For CZPT F-150 2009-2014 |
F81Z4A376HA |
For CZPT F-350 Tremendous Obligation 99-06 |
|
sixty five-9300 |
For CZPT Excursion 2001-2003 |
5C3Z4A376FA |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Obligation 99-ten |
|
65-9463 |
For CZPT ESCAPE 2001-2005 |
7C194K357HB |
For CZPT Transit 2000-2006 |
|
sixty five-9440 |
For CZPT CZPT 1983-1987 |
5C3Z4A376G |
For CZPT F250 Tremendous Duty 99-04 |
|
sixty five-9110 |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Responsibility 99-02 |
7C19-4K145-BB |
For CZPT Transit |
|
sixty five-9114 |
For CZPT F-350 Super Responsibility ninety nine-02 |
7C19-4K145-DB |
For CZPT Transit 2015-2016 |
|
65-9116 |
For CZPT F-250 Tremendous Obligation 99-02 |
5L834K145BA |
For CZPT Escape 2013-2017 |
|
sixty five-9442 |
For CZPT CZPT 1988-1990 |
AL3Z4A376D |
For CZPT Expedition 2007-2014 |
|
sixty five-9443 |
For CZPT CZPT 1988-1996 |
7A2Z4R602N |
For CZPT Explorer Activity Trac 07-ten |
|
65-9444 |
For CZPT CZPT 1990-1996 |
938-082 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2009-2014 |
|
sixty five-9544 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 2004 |
sixty five-9441 |
For CZPT CZPT 1988-1993 |
|
sixty five-9545 |
For CZPT F-a hundred and fifty 1999-2003 |
65-2001 |
For CZPT Expedition 2006-2014 |
|
sixty five-2000 |
9C3Z4A376C |
1L244A376A |
5L3Z-4R602-W |
|
sixty five-2002 |
AE5Z4R602A |
1L244A376AA |
5L3Z-4R602-WA |
|
sixty five-2003 |
AL344K145KB |
1L244A376AD |
5L3Z-4R602-WB |
|
sixty five-2004 |
AL3Z4A376C |
1L244A376AE |
5L3Z4R602ZA |
|
sixty five-2005 |
AL3Z4R602KB |
1L244A376AF |
5L3Z4R602ZB |
|
65-2011 |
BC3Z-4A376-A |
1L2Z4A376AA |
5L5Z4602B |
|
sixty five-2012 |
BL3V-4602-BD |
1L2Z-4A376-AA |
5L8Z4R602BA |
|
65-2013 |
BL3Z4R602H |
2C3Z4R602FB |
6F934K145AC |
|
sixty five-2015 |
BL8Z4R602A |
2L1Z4A376AA |
6L344K145BG |
|
65-2016 |
CN4C154K145AD |
2L8Z4R602AA |
6L34-4K145-HB |
|
sixty five-9157 |
CN4D154K357AD |
3C3Z4A376AA |
6L34-4K145-HC |
|
65-9159 |
DL3Z4R602AH |
3L8Z4R602BA |
6L34-4K145-KC |
|
sixty five-9293 |
DL3Z4R602AL |
4L34-4K145-PD |
6L34-4K145-TF |
|
sixty five-9294 |
DL3Z4R602B |
4L34-4K145-TF |
6L34-4K145-WB |
|
sixty five-9450 |
DL3Z4R602E |
4L34-4K145-WA |
6L3Z4R602Z |
|
65-9451 |
DL3Z4R602Q |
4L34-4K145-WC |
6L8Z4R602B |
|
sixty five-9462 |
DL3Z4R602T |
5C3Z4A376A |
6R3Z4602B |
|
sixty five-9543 |
DT4Z4R602A |
5C3Z4A376AA |
7A2Z4R602D |
|
938-063 |
DV61-4K145-AC |
5C3Z4A376CA |
7A2Z4R602G |
|
938-076 |
E5TZ4A376C |
5C3Z4A376DA |
7A2Z4R602K |
|
938-091 |
E9TA4376DA |
5C3Z4A376EA |
7C19-4K145DB |
|
938-199 |
F0TA4602ZA |
5C3Z4A376F |
7L1Z4A376A |
|
938-301 |
F1TZ4602-two |
5C3Z4A376JA |
7L1Z4A376B |
|
938-305 |
F2G34K145CC |
5C3Z4A376LA |
7L344K145BA |
|
938-801 |
F37A4A376BB |
5C3Z4A376NA |
7L34-4K145-BA |
|
938-802 |
F65Z4602EA |
5L34-4K145-PA |
7L34-4K145-TA |
|
946-821 |
F65Z4602NB |
5L34-4K145-PD |
7L34-4K145-WA |
|
946-830 |
F77A4376CB |
5L34-4K145-RA |
7L3Z-4R602-C |
|
976-698 |
F81Z4A376KA |
5L34-4K145-TA |
7L3Z-4R602-J |
|
936-285 |
F81Z4A376MA |
5L34-4K145-TC |
7L8Z4R602B |
|
936-288 |
F81Z4A376NA |
5L34-4K145-TD |
7L8Z-4R602-B |
|
936-325 |
F81Z4A376PA |
5L34-4K145-VA |
7R3Z-4602-A |
|
936-327 |
F81Z4R602FL |
5L34-4K145-VC |
8E5Z4R602A |
|
936-800 |
FG1Z4R602A |
5L34-4K145-WB |
8L34-4K145-TA |
|
936-801 |
SA5525100A |
5L34-4K145-WC |
8L34-4K145-VA |
|
936-803 |
SA5525100E |
5L34-4K145-WD |
8L3Z-4602-D |
|
936-806 |
SA5525100F |
5L3Z4A376A |
8L3Z-4R602-B |
|
936-808 |
SA5525100L |
5L3Z4R602BB |
8L3Z-4R602-C |
|
936-810 |
SA5525100M |
5L3Z-4R602-T |
8L3Z-4R602-D |
|
936-811 |
SA5625100K |
5L3Z-4R602-TC |
8L3Z4R602-E |
|
936-813 |
SA5625100L |
YL8Z4602AH |
8L3Z-4R602-F |
|
936-846 |
SA60E-twenty five-100AC |
YL8Z4602AJ |
8L3Z4R602G |
|
936-891 |
SA7125100 |
YL8Z4602BH |
8L3Z-4R602-H |
|
936-896 |
XL2Z4A376AA |
YL8Z4602BJ |
8L844K145DA |
|
936-942 |
XL2Z-4A376-BA |
ZZC571100A |
YC3Z4A376VA |
|
936-973 |
XL2Z4A376BB |
ZZL571500 |
YC3Z4A376WA |
|
938-031 |
YC3W4A376AB |
ZZP325100 |
YL844602AM |
|
65-9731 |
YC3Z4A376AA |
YC3Z4A376SA |
YL844602BH |
|
65-9293 |
YC3Z4A376AB |
YC3Z4A376TA |
YL844602BM |
|
65-9713 |
YC3Z4A376RA |
YC3Z4A376CA |
65-9294 |
If you need to have a lot more details about FORD Propeller Shaft, remember to information or email to us ASAP.
—- OUR Gain —-
+seven-hundred designs for The usa & EUROPE market placeMOQ: 3PCS / for 1 item, MIN get sum: USD5000
Top quality assurance: One particular Calendar year WarrantySteady shipping time: 45 days
Totally free Sample DesignedApply O/A thirty-90 times for regular client
Becides CZPT Propeller Shaft,we have In excess of seven-hundred items relevant for subsequent cars:
—- F A Q —-
Q1: If we do not locate what we require on your site, what must we do?
You can deliver us the OE amount or of the product you want, we will examine if we have them.
We also produce new types in accordance to customer’s need
you can get in touch with us for more detail.
Q2: Can I get a price price reduction if I buy large portions?Of course, it depends on your purchasing quantity, much more quantity more discount.
Q3: What about the delivery time?If we have stock, we can send out you the items within 3 functioning times,
if we will not have stock, normally it requirements ten to 40 times.
Q4: What is actually our MOQ?Sample get for quality tests 1 piece , normal purchase fifty items for 1 purchase with blended models .
Q5: What’s your payment phrases and situation ?We can take T/T , LC, Trade Assurance, Western Union, Paypal, Moneygram ect.
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Ford |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
|
Product Name
|
Front Prop Drive Shaft Assembly For Ford Explorer 97-01, Mountaineer V8 5.0L 4WD
|
|
Part Number
|
65-9450, 65-9294, F77A4A376CB, 936-325, XL2Z4A376BB
|
|
Vehicle Fitment
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1997-2001
For MERCURY MOUNTAINEER 1997-1998 |
|
Compressed Length
|
28.46"
|
|
MOQ
|
1pc if we have them in stock
|
|
Delivery time
|
1-7 days for stock items, 25 days for production items
|
|
Note
|
Have stock in China and US!
|
###
|
OE NO.
|
APPLICATION
|
OE NO.
|
APPLICATION
|
|
65-9152
|
For FORD Bronco 1966-1970
|
7L3Z 4R602-J
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
|
65-9153
|
For FORD Bronco 1966-1977
|
4L34-4K145-RE
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2009
|
|
65-9148
|
For FORD F-250 1977-1979
|
4L34-4K145-RA
|
For FORD Lobo 2004-2010
|
|
65-9170
|
For FORD Bronco 1978
|
6F9Z4R602A
|
For FORD Five Hundred 05-07
|
|
65-9164
|
For FORD Bronco 1979
|
5F9Z4R602AA
|
For FORD Freestyle 2005-2007
|
|
65-9166
|
For FORD Bronco 1979
|
6F924R602-A
|
For FORD Five Hundred 05-07
|
|
65-9161
|
For FORD Bronco 1979
|
5F934K145AE
|
For FORD Freestyle 2005-2007
|
|
65-9158
|
For FORD F-150 1979
|
936-812
|
For FORD Mustang 2005-2008
|
|
65-9160
|
For FORD Bronco 1980-1982
|
8L3Z4R602H
|
For FORD F-150 2006-2008
|
|
65-9832
|
For FORD Bronco 1983-1984
|
936-807
|
For FORD F-150 2006-2008
|
|
65-9830
|
For FORD Ranger 1983-1985
|
8L3Z4R602B
|
For FORD LOBO 2006-2008
|
|
65-9831
|
For FORD Ranger 1983-1985
|
7L3Z4R602K
|
For FORD F-150 2006-2008
|
|
65-9821
|
For FORD Bronco II 1984-1990
|
CN4C154K357AD
|
For FORD Transit 2006-2014
|
|
65-9822
|
For FORD Bronco II 1984-1990
|
7T434K357AC
|
For FORD Edge 2007-2008
|
|
65-9430
|
For FORD Bronco 1985-1986
|
6L2Z4A376B
|
For FORD Expedition 2007-2009
|
|
65-9423
|
For FORD Ranger 1985-1988
|
7T4Z4R602A
|
For FORD Edge 2007-2013
|
|
65-9431
|
For FORD Bronco 1985-1989
|
936-847
|
For FORD TAURUS X 2008-2009
|
|
65-9721
|
For FORD F-350 1985-1994
|
8L8Z4R602C
|
For FORD Escape 2008-2012
|
|
65-9416
|
For FORD Bronco 1987-1989
|
936-892
|
For FORD ESCAPE 2008-2012
|
|
65-9400
|
For FORD Bronco 1987-1989
|
7E5Z4R602A
|
For FORD FUSION 2008-2012
|
|
65-9636
|
For FORD Ranger 1988
|
8G1Z4R602A
|
For FORD Taurus 2008-2015
|
|
65-9638
|
For FORD Ranger 1988-1989
|
936-809
|
For FORD F-150 2010-2011
|
|
65-9823
|
For FORD Bronco II 1989-1990
|
AL344K145KA
|
For FORD LOBO 2010-2011
|
|
65-9739
|
For FORD F-350 1989-1994
|
946-831
|
For FORD F-150 2011-2014
|
|
65-9667
|
For FORD F-350 1989-1994
|
BL3V4602BD
|
For FORD F-150 2011-2014
|
|
938-066
|
For FORD F-250 1989-1997
|
8G1Z4R602B
|
For FORD Explorer 2011-2015
|
|
65-9664
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1993
|
BC3Z4A376A
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 11-16
|
|
65-9665
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1994
|
5L834K145BA
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2017
|
|
65-9662
|
For FORD RANGER 1990-1994
|
7C19-4K145-DB
|
For FORD Transit 2015-2016
|
|
65-9660
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1996
|
7C19-4K145-BB
|
For FORD Transit
|
|
65-9663
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1996
|
7C19-4K145-DB
|
For FORD Transit 2015-2016
|
|
65-9443
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1996
|
5L834K145BA
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2017
|
|
65-9444
|
For FORD BRONCO 1990-1996
|
AL3Z4A376D
|
For FORD Expedition 2007-2014
|
|
65-9661
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1991-1994
|
5C3Z4A376G
|
For FORD F250 Super Duty 99-04
|
|
65-9624
|
For FORD Explorer 1995-1996
|
CV6Z4R602B
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2016
|
|
65-9447
|
For FORD F-350 1995-1996
|
4641968AE
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2016
|
|
65-9449
|
For FORD F-350 1995-1996
|
BL3Z4R602D
|
For FORD F150 2011-2012
|
|
65-9675
|
For FORD Ranger 1995-1997
|
ZZR0-25-100
|
For FORD Explorer Sport Trac 05
|
|
65-9672
|
For FORD F-100 1996-1997
|
2L8Z4R602BA
|
For FORD Escape 2001-2007
|
|
65-9453
|
For FORD F-150 1997-1998
|
XL2Z-4A376-AA
|
For FORD Explorer Sport 2002-2003
|
|
65-9544
|
For FORD F-150 2004
|
1L2Z4A376A
|
For FORD EXPLORER 2002-2010
|
|
65-9545
|
For FORD F-150 1999-2003
|
936-805
|
For FORD F-150 2004
|
|
65-9441
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1993
|
8L3Z4R602E
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
|
65-2001
|
For FORD EXPEDITION 06-14
|
8L3Z4R602F
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
|
65-9305
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-01
|
65-9302
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2001-2005
|
|
65-9112
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
E9TZ4A376B
|
For FORD BRONCO 1990-1996
|
|
65-9115
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
F6TZ4A376RA
|
For FORD F-150 1990-1996
|
|
938-304
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 11-16
|
F77A4376BB
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1997-2001
|
|
936-802
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
F75Z4A376BB
|
For FORD Expedition 1997-2002
|
|
65-9546
|
For FORD Excursion 2001-2005
|
F77Z4A376CB
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1998-2001
|
|
946-448
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 02-03
|
5L544602DB
|
For FORD Ranger 1998-2011
|
|
65-9304
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2000-2003
|
5C3Z4A376D
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-06
|
|
65-9303
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2000-2003
|
YC3Z4A376EA
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 99-06
|
|
938-082
|
For FORD F-150 2009-2014
|
F81Z4A376HA
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 99-06
|
|
65-9300
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2001-2003
|
5C3Z4A376FA
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-10
|
|
65-9463
|
For FORD ESCAPE 2001-2005
|
7C194K357HB
|
For FORD Transit 2000-2006
|
|
65-9440
|
For FORD BRONCO 1983-1987
|
5C3Z4A376G
|
For FORD F250 Super Duty 99-04
|
|
65-9110
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
7C19-4K145-BB
|
For FORD Transit
|
|
65-9114
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 99-02
|
7C19-4K145-DB
|
For FORD Transit 2015-2016
|
|
65-9116
|
For Ford F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
5L834K145BA
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2017
|
|
65-9442
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1990
|
AL3Z4A376D
|
For FORD Expedition 2007-2014
|
|
65-9443
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1996
|
7A2Z4R602N
|
For FORD Explorer Sport Trac 07-10
|
|
65-9444
|
For FORD BRONCO 1990-1996
|
938-082
|
For FORD F-150 2009-2014
|
|
65-9544
|
For FORD F-150 2004
|
65-9441
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1993
|
|
65-9545
|
For FORD F-150 1999-2003
|
65-2001
|
For FORD Expedition 2006-2014
|
|
65-2000
|
9C3Z4A376C
|
1L244A376A
|
5L3Z-4R602-W
|
|
65-2002
|
AE5Z4R602A
|
1L244A376AA
|
5L3Z-4R602-WA
|
|
65-2003
|
AL344K145KB
|
1L244A376AD
|
5L3Z-4R602-WB
|
|
65-2004
|
AL3Z4A376C
|
1L244A376AE
|
5L3Z4R602ZA
|
|
65-2005
|
AL3Z4R602KB
|
1L244A376AF
|
5L3Z4R602ZB
|
|
65-2011
|
BC3Z-4A376-A
|
1L2Z4A376AA
|
5L5Z4602B
|
|
65-2012
|
BL3V-4602-BD
|
1L2Z-4A376-AA
|
5L8Z4R602BA
|
|
65-2013
|
BL3Z4R602H
|
2C3Z4R602FB
|
6F934K145AC
|
|
65-2015
|
BL8Z4R602A
|
2L1Z4A376AA
|
6L344K145BG
|
|
65-2016
|
CN4C154K145AD
|
2L8Z4R602AA
|
6L34-4K145-HB
|
|
65-9157
|
CN4D154K357AD
|
3C3Z4A376AA
|
6L34-4K145-HC
|
|
65-9159
|
DL3Z4R602AH
|
3L8Z4R602BA
|
6L34-4K145-KC
|
|
65-9293
|
DL3Z4R602AL
|
4L34-4K145-PD
|
6L34-4K145-TF
|
|
65-9294
|
DL3Z4R602B
|
4L34-4K145-TF
|
6L34-4K145-WB
|
|
65-9450
|
DL3Z4R602E
|
4L34-4K145-WA
|
6L3Z4R602Z
|
|
65-9451
|
DL3Z4R602Q
|
4L34-4K145-WC
|
6L8Z4R602B
|
|
65-9462
|
DL3Z4R602T
|
5C3Z4A376A
|
6R3Z4602B
|
|
65-9543
|
DT4Z4R602A
|
5C3Z4A376AA
|
7A2Z4R602D
|
|
938-063
|
DV61-4K145-AC
|
5C3Z4A376CA
|
7A2Z4R602G
|
|
938-076
|
E5TZ4A376C
|
5C3Z4A376DA
|
7A2Z4R602K
|
|
938-091
|
E9TA4376DA
|
5C3Z4A376EA
|
7C19-4K145DB
|
|
938-199
|
F0TA4602ZA
|
5C3Z4A376F
|
7L1Z4A376A
|
|
938-301
|
F1TZ4602-2
|
5C3Z4A376JA
|
7L1Z4A376B
|
|
938-305
|
F2G34K145CC
|
5C3Z4A376LA
|
7L344K145BA
|
|
938-801
|
F37A4A376BB
|
5C3Z4A376NA
|
7L34-4K145-BA
|
|
938-802
|
F65Z4602EA
|
5L34-4K145-PA
|
7L34-4K145-TA
|
|
946-821
|
F65Z4602NB
|
5L34-4K145-PD
|
7L34-4K145-WA
|
|
946-830
|
F77A4376CB
|
5L34-4K145-RA
|
7L3Z-4R602-C
|
|
976-698
|
F81Z4A376KA
|
5L34-4K145-TA
|
7L3Z-4R602-J
|
|
936-285
|
F81Z4A376MA
|
5L34-4K145-TC
|
7L8Z4R602B
|
|
936-288
|
F81Z4A376NA
|
5L34-4K145-TD
|
7L8Z-4R602-B
|
|
936-325
|
F81Z4A376PA
|
5L34-4K145-VA
|
7R3Z-4602-A
|
|
936-327
|
F81Z4R602FL
|
5L34-4K145-VC
|
8E5Z4R602A
|
|
936-800
|
FG1Z4R602A
|
5L34-4K145-WB
|
8L34-4K145-TA
|
|
936-801
|
SA5525100A
|
5L34-4K145-WC
|
8L34-4K145-VA
|
|
936-803
|
SA5525100E
|
5L34-4K145-WD
|
8L3Z-4602-D
|
|
936-806
|
SA5525100F
|
5L3Z4A376A
|
8L3Z-4R602-B
|
|
936-808
|
SA5525100L
|
5L3Z4R602BB
|
8L3Z-4R602-C
|
|
936-810
|
SA5525100M
|
5L3Z-4R602-T
|
8L3Z-4R602-D
|
|
936-811
|
SA5625100K
|
5L3Z-4R602-TC
|
8L3Z4R602-E
|
|
936-813
|
SA5625100L
|
YL8Z4602AH
|
8L3Z-4R602-F
|
|
936-846
|
SA60E-25-100AC
|
YL8Z4602AJ
|
8L3Z4R602G
|
|
936-891
|
SA7125100
|
YL8Z4602BH
|
8L3Z-4R602-H
|
|
936-896
|
XL2Z4A376AA
|
YL8Z4602BJ
|
8L844K145DA
|
|
936-942
|
XL2Z-4A376-BA
|
ZZC025100A
|
YC3Z4A376VA
|
|
936-973
|
XL2Z4A376BB
|
ZZL025500
|
YC3Z4A376WA
|
|
938-031
|
YC3W4A376AB
|
ZZP325100
|
YL844602AM
|
|
65-9731
|
YC3Z4A376AA
|
YC3Z4A376SA
|
YL844602BH
|
|
65-9293
|
YC3Z4A376AB
|
YC3Z4A376TA
|
YL844602BM
|
|
65-9713
|
YC3Z4A376RA
|
YC3Z4A376CA
|
65-9294
|
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Ford |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
|
Product Name
|
Front Prop Drive Shaft Assembly For Ford Explorer 97-01, Mountaineer V8 5.0L 4WD
|
|
Part Number
|
65-9450, 65-9294, F77A4A376CB, 936-325, XL2Z4A376BB
|
|
Vehicle Fitment
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1997-2001
For MERCURY MOUNTAINEER 1997-1998 |
|
Compressed Length
|
28.46"
|
|
MOQ
|
1pc if we have them in stock
|
|
Delivery time
|
1-7 days for stock items, 25 days for production items
|
|
Note
|
Have stock in China and US!
|
###
|
OE NO.
|
APPLICATION
|
OE NO.
|
APPLICATION
|
|
65-9152
|
For FORD Bronco 1966-1970
|
7L3Z 4R602-J
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
|
65-9153
|
For FORD Bronco 1966-1977
|
4L34-4K145-RE
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2009
|
|
65-9148
|
For FORD F-250 1977-1979
|
4L34-4K145-RA
|
For FORD Lobo 2004-2010
|
|
65-9170
|
For FORD Bronco 1978
|
6F9Z4R602A
|
For FORD Five Hundred 05-07
|
|
65-9164
|
For FORD Bronco 1979
|
5F9Z4R602AA
|
For FORD Freestyle 2005-2007
|
|
65-9166
|
For FORD Bronco 1979
|
6F924R602-A
|
For FORD Five Hundred 05-07
|
|
65-9161
|
For FORD Bronco 1979
|
5F934K145AE
|
For FORD Freestyle 2005-2007
|
|
65-9158
|
For FORD F-150 1979
|
936-812
|
For FORD Mustang 2005-2008
|
|
65-9160
|
For FORD Bronco 1980-1982
|
8L3Z4R602H
|
For FORD F-150 2006-2008
|
|
65-9832
|
For FORD Bronco 1983-1984
|
936-807
|
For FORD F-150 2006-2008
|
|
65-9830
|
For FORD Ranger 1983-1985
|
8L3Z4R602B
|
For FORD LOBO 2006-2008
|
|
65-9831
|
For FORD Ranger 1983-1985
|
7L3Z4R602K
|
For FORD F-150 2006-2008
|
|
65-9821
|
For FORD Bronco II 1984-1990
|
CN4C154K357AD
|
For FORD Transit 2006-2014
|
|
65-9822
|
For FORD Bronco II 1984-1990
|
7T434K357AC
|
For FORD Edge 2007-2008
|
|
65-9430
|
For FORD Bronco 1985-1986
|
6L2Z4A376B
|
For FORD Expedition 2007-2009
|
|
65-9423
|
For FORD Ranger 1985-1988
|
7T4Z4R602A
|
For FORD Edge 2007-2013
|
|
65-9431
|
For FORD Bronco 1985-1989
|
936-847
|
For FORD TAURUS X 2008-2009
|
|
65-9721
|
For FORD F-350 1985-1994
|
8L8Z4R602C
|
For FORD Escape 2008-2012
|
|
65-9416
|
For FORD Bronco 1987-1989
|
936-892
|
For FORD ESCAPE 2008-2012
|
|
65-9400
|
For FORD Bronco 1987-1989
|
7E5Z4R602A
|
For FORD FUSION 2008-2012
|
|
65-9636
|
For FORD Ranger 1988
|
8G1Z4R602A
|
For FORD Taurus 2008-2015
|
|
65-9638
|
For FORD Ranger 1988-1989
|
936-809
|
For FORD F-150 2010-2011
|
|
65-9823
|
For FORD Bronco II 1989-1990
|
AL344K145KA
|
For FORD LOBO 2010-2011
|
|
65-9739
|
For FORD F-350 1989-1994
|
946-831
|
For FORD F-150 2011-2014
|
|
65-9667
|
For FORD F-350 1989-1994
|
BL3V4602BD
|
For FORD F-150 2011-2014
|
|
938-066
|
For FORD F-250 1989-1997
|
8G1Z4R602B
|
For FORD Explorer 2011-2015
|
|
65-9664
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1993
|
BC3Z4A376A
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 11-16
|
|
65-9665
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1994
|
5L834K145BA
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2017
|
|
65-9662
|
For FORD RANGER 1990-1994
|
7C19-4K145-DB
|
For FORD Transit 2015-2016
|
|
65-9660
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1996
|
7C19-4K145-BB
|
For FORD Transit
|
|
65-9663
|
For FORD Bronco 1990-1996
|
7C19-4K145-DB
|
For FORD Transit 2015-2016
|
|
65-9443
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1996
|
5L834K145BA
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2017
|
|
65-9444
|
For FORD BRONCO 1990-1996
|
AL3Z4A376D
|
For FORD Expedition 2007-2014
|
|
65-9661
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1991-1994
|
5C3Z4A376G
|
For FORD F250 Super Duty 99-04
|
|
65-9624
|
For FORD Explorer 1995-1996
|
CV6Z4R602B
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2016
|
|
65-9447
|
For FORD F-350 1995-1996
|
4641968AE
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2016
|
|
65-9449
|
For FORD F-350 1995-1996
|
BL3Z4R602D
|
For FORD F150 2011-2012
|
|
65-9675
|
For FORD Ranger 1995-1997
|
ZZR0-25-100
|
For FORD Explorer Sport Trac 05
|
|
65-9672
|
For FORD F-100 1996-1997
|
2L8Z4R602BA
|
For FORD Escape 2001-2007
|
|
65-9453
|
For FORD F-150 1997-1998
|
XL2Z-4A376-AA
|
For FORD Explorer Sport 2002-2003
|
|
65-9544
|
For FORD F-150 2004
|
1L2Z4A376A
|
For FORD EXPLORER 2002-2010
|
|
65-9545
|
For FORD F-150 1999-2003
|
936-805
|
For FORD F-150 2004
|
|
65-9441
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1993
|
8L3Z4R602E
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
|
65-2001
|
For FORD EXPEDITION 06-14
|
8L3Z4R602F
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
|
65-9305
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-01
|
65-9302
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2001-2005
|
|
65-9112
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
E9TZ4A376B
|
For FORD BRONCO 1990-1996
|
|
65-9115
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
F6TZ4A376RA
|
For FORD F-150 1990-1996
|
|
938-304
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 11-16
|
F77A4376BB
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1997-2001
|
|
936-802
|
For FORD F-150 2004-2008
|
F75Z4A376BB
|
For FORD Expedition 1997-2002
|
|
65-9546
|
For FORD Excursion 2001-2005
|
F77Z4A376CB
|
For FORD EXPLORER 1998-2001
|
|
946-448
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 02-03
|
5L544602DB
|
For FORD Ranger 1998-2011
|
|
65-9304
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2000-2003
|
5C3Z4A376D
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-06
|
|
65-9303
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2000-2003
|
YC3Z4A376EA
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 99-06
|
|
938-082
|
For FORD F-150 2009-2014
|
F81Z4A376HA
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 99-06
|
|
65-9300
|
For FORD EXCURSION 2001-2003
|
5C3Z4A376FA
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-10
|
|
65-9463
|
For FORD ESCAPE 2001-2005
|
7C194K357HB
|
For FORD Transit 2000-2006
|
|
65-9440
|
For FORD BRONCO 1983-1987
|
5C3Z4A376G
|
For FORD F250 Super Duty 99-04
|
|
65-9110
|
For FORD F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
7C19-4K145-BB
|
For FORD Transit
|
|
65-9114
|
For FORD F-350 Super Duty 99-02
|
7C19-4K145-DB
|
For FORD Transit 2015-2016
|
|
65-9116
|
For Ford F-250 Super Duty 99-02
|
5L834K145BA
|
For FORD Escape 2013-2017
|
|
65-9442
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1990
|
AL3Z4A376D
|
For FORD Expedition 2007-2014
|
|
65-9443
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1996
|
7A2Z4R602N
|
For FORD Explorer Sport Trac 07-10
|
|
65-9444
|
For FORD BRONCO 1990-1996
|
938-082
|
For FORD F-150 2009-2014
|
|
65-9544
|
For FORD F-150 2004
|
65-9441
|
For FORD BRONCO 1988-1993
|
|
65-9545
|
For FORD F-150 1999-2003
|
65-2001
|
For FORD Expedition 2006-2014
|
|
65-2000
|
9C3Z4A376C
|
1L244A376A
|
5L3Z-4R602-W
|
|
65-2002
|
AE5Z4R602A
|
1L244A376AA
|
5L3Z-4R602-WA
|
|
65-2003
|
AL344K145KB
|
1L244A376AD
|
5L3Z-4R602-WB
|
|
65-2004
|
AL3Z4A376C
|
1L244A376AE
|
5L3Z4R602ZA
|
|
65-2005
|
AL3Z4R602KB
|
1L244A376AF
|
5L3Z4R602ZB
|
|
65-2011
|
BC3Z-4A376-A
|
1L2Z4A376AA
|
5L5Z4602B
|
|
65-2012
|
BL3V-4602-BD
|
1L2Z-4A376-AA
|
5L8Z4R602BA
|
|
65-2013
|
BL3Z4R602H
|
2C3Z4R602FB
|
6F934K145AC
|
|
65-2015
|
BL8Z4R602A
|
2L1Z4A376AA
|
6L344K145BG
|
|
65-2016
|
CN4C154K145AD
|
2L8Z4R602AA
|
6L34-4K145-HB
|
|
65-9157
|
CN4D154K357AD
|
3C3Z4A376AA
|
6L34-4K145-HC
|
|
65-9159
|
DL3Z4R602AH
|
3L8Z4R602BA
|
6L34-4K145-KC
|
|
65-9293
|
DL3Z4R602AL
|
4L34-4K145-PD
|
6L34-4K145-TF
|
|
65-9294
|
DL3Z4R602B
|
4L34-4K145-TF
|
6L34-4K145-WB
|
|
65-9450
|
DL3Z4R602E
|
4L34-4K145-WA
|
6L3Z4R602Z
|
|
65-9451
|
DL3Z4R602Q
|
4L34-4K145-WC
|
6L8Z4R602B
|
|
65-9462
|
DL3Z4R602T
|
5C3Z4A376A
|
6R3Z4602B
|
|
65-9543
|
DT4Z4R602A
|
5C3Z4A376AA
|
7A2Z4R602D
|
|
938-063
|
DV61-4K145-AC
|
5C3Z4A376CA
|
7A2Z4R602G
|
|
938-076
|
E5TZ4A376C
|
5C3Z4A376DA
|
7A2Z4R602K
|
|
938-091
|
E9TA4376DA
|
5C3Z4A376EA
|
7C19-4K145DB
|
|
938-199
|
F0TA4602ZA
|
5C3Z4A376F
|
7L1Z4A376A
|
|
938-301
|
F1TZ4602-2
|
5C3Z4A376JA
|
7L1Z4A376B
|
|
938-305
|
F2G34K145CC
|
5C3Z4A376LA
|
7L344K145BA
|
|
938-801
|
F37A4A376BB
|
5C3Z4A376NA
|
7L34-4K145-BA
|
|
938-802
|
F65Z4602EA
|
5L34-4K145-PA
|
7L34-4K145-TA
|
|
946-821
|
F65Z4602NB
|
5L34-4K145-PD
|
7L34-4K145-WA
|
|
946-830
|
F77A4376CB
|
5L34-4K145-RA
|
7L3Z-4R602-C
|
|
976-698
|
F81Z4A376KA
|
5L34-4K145-TA
|
7L3Z-4R602-J
|
|
936-285
|
F81Z4A376MA
|
5L34-4K145-TC
|
7L8Z4R602B
|
|
936-288
|
F81Z4A376NA
|
5L34-4K145-TD
|
7L8Z-4R602-B
|
|
936-325
|
F81Z4A376PA
|
5L34-4K145-VA
|
7R3Z-4602-A
|
|
936-327
|
F81Z4R602FL
|
5L34-4K145-VC
|
8E5Z4R602A
|
|
936-800
|
FG1Z4R602A
|
5L34-4K145-WB
|
8L34-4K145-TA
|
|
936-801
|
SA5525100A
|
5L34-4K145-WC
|
8L34-4K145-VA
|
|
936-803
|
SA5525100E
|
5L34-4K145-WD
|
8L3Z-4602-D
|
|
936-806
|
SA5525100F
|
5L3Z4A376A
|
8L3Z-4R602-B
|
|
936-808
|
SA5525100L
|
5L3Z4R602BB
|
8L3Z-4R602-C
|
|
936-810
|
SA5525100M
|
5L3Z-4R602-T
|
8L3Z-4R602-D
|
|
936-811
|
SA5625100K
|
5L3Z-4R602-TC
|
8L3Z4R602-E
|
|
936-813
|
SA5625100L
|
YL8Z4602AH
|
8L3Z-4R602-F
|
|
936-846
|
SA60E-25-100AC
|
YL8Z4602AJ
|
8L3Z4R602G
|
|
936-891
|
SA7125100
|
YL8Z4602BH
|
8L3Z-4R602-H
|
|
936-896
|
XL2Z4A376AA
|
YL8Z4602BJ
|
8L844K145DA
|
|
936-942
|
XL2Z-4A376-BA
|
ZZC025100A
|
YC3Z4A376VA
|
|
936-973
|
XL2Z4A376BB
|
ZZL025500
|
YC3Z4A376WA
|
|
938-031
|
YC3W4A376AB
|
ZZP325100
|
YL844602AM
|
|
65-9731
|
YC3Z4A376AA
|
YC3Z4A376SA
|
YL844602BH
|
|
65-9293
|
YC3Z4A376AB
|
YC3Z4A376TA
|
YL844602BM
|
|
65-9713
|
YC3Z4A376RA
|
YC3Z4A376CA
|
65-9294
|
Guide to Drive Shafts and U-Joints
If you’re concerned about the performance of your car’s driveshaft, you’re not alone. Many car owners are unaware of the warning signs of a failed driveshaft, but knowing what to look for can help you avoid costly repairs. Here is a brief guide on drive shafts, U-joints and maintenance intervals. Listed below are key points to consider before replacing a vehicle driveshaft.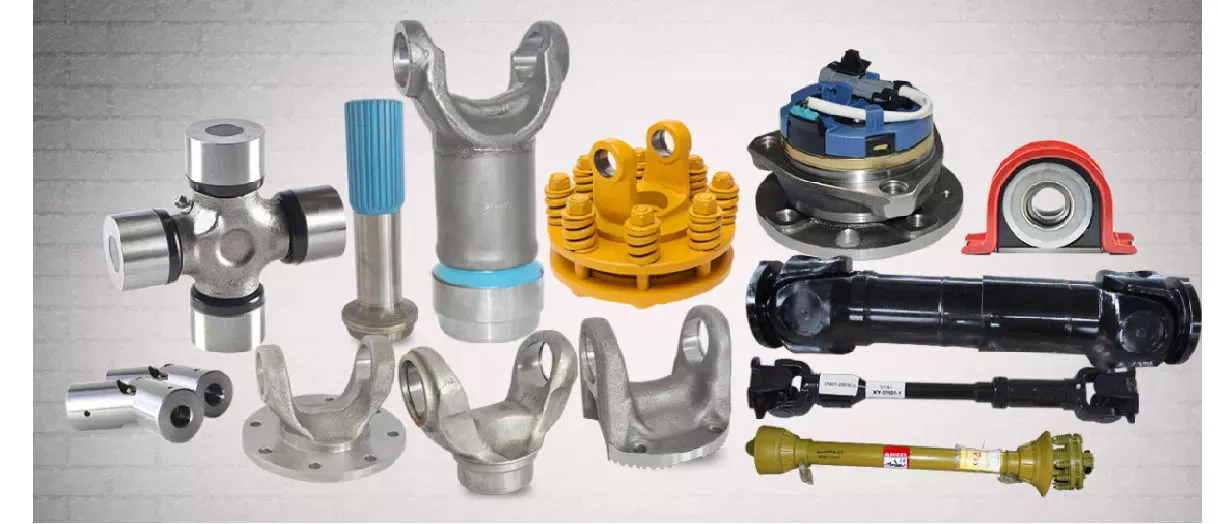
Symptoms of Driveshaft Failure
Identifying a faulty driveshaft is easy if you’ve ever heard a strange noise from under your car. These sounds are caused by worn U-joints and bearings supporting the drive shaft. When they fail, the drive shafts stop rotating properly, creating a clanking or squeaking sound. When this happens, you may hear noise from the side of the steering wheel or floor.
In addition to noise, a faulty driveshaft can cause your car to swerve in tight corners. It can also lead to suspended bindings that limit overall control. Therefore, you should have these symptoms checked by a mechanic as soon as you notice them. If you notice any of the symptoms above, your next step should be to tow your vehicle to a mechanic. To avoid extra trouble, make sure you’ve taken precautions by checking your car’s oil level.
In addition to these symptoms, you should also look for any noise from the drive shaft. The first thing to look for is the squeak. This was caused by severe damage to the U-joint attached to the drive shaft. In addition to noise, you should also look for rust on the bearing cap seals. In extreme cases, your car can even shudder when accelerating.
Vibration while driving can be an early warning sign of a driveshaft failure. Vibration can be due to worn bushings, stuck sliding yokes, or even springs or bent yokes. Excessive torque can be caused by a worn center bearing or a damaged U-joint. The vehicle may make unusual noises in the chassis system.
If you notice these signs, it’s time to take your car to a mechanic. You should check regularly, especially heavy vehicles. If you’re not sure what’s causing the noise, check your car’s transmission, engine, and rear differential. If you suspect that a driveshaft needs to be replaced, a certified mechanic can replace the driveshaft in your car.
Drive shaft type
Driveshafts are used in many different types of vehicles. These include four-wheel drive, front-engine rear-wheel drive, motorcycles and boats. Each type of drive shaft has its own purpose. Below is an overview of the three most common types of drive shafts:
The driveshaft is a circular, elongated shaft that transmits torque from the engine to the wheels. Drive shafts often contain many joints to compensate for changes in length or angle. Some drive shafts also include connecting shafts and internal constant velocity joints. Some also include torsional dampers, spline joints, and even prismatic joints. The most important thing about the driveshaft is that it plays a vital role in transmitting torque from the engine to the wheels.
The drive shaft needs to be both light and strong to move torque. While steel is the most commonly used material for automotive driveshafts, other materials such as aluminum, composites, and carbon fiber are also commonly used. It all depends on the purpose and size of the vehicle. Precision Manufacturing is a good source for OEM products and OEM driveshafts. So when you’re looking for a new driveshaft, keep these factors in mind when buying.
Cardan joints are another common drive shaft. A universal joint, also known as a U-joint, is a flexible coupling that allows one shaft to drive the other at an angle. This type of drive shaft allows power to be transmitted while the angle of the other shaft is constantly changing. While a gimbal is a good option, it’s not a perfect solution for all applications.
CZPT, Inc. has state-of-the-art machinery to service all types of drive shafts, from small cars to race cars. They serve a variety of needs, including racing, industry and agriculture. Whether you need a new drive shaft or a simple adjustment, the staff at CZPT can meet all your needs. You’ll be back on the road soon!
U-joint
If your car yoke or u-joint shows signs of wear, it’s time to replace them. The easiest way to replace them is to follow the steps below. Use a large flathead screwdriver to test. If you feel any movement, the U-joint is faulty. Also, inspect the bearing caps for damage or rust. If you can’t find the u-joint wrench, try checking with a flashlight.
When inspecting U-joints, make sure they are properly lubricated and lubricated. If the joint is dry or poorly lubricated, it can quickly fail and cause your car to squeak while driving. Another sign that a joint is about to fail is a sudden, excessive whine. Check your u-joints every year or so to make sure they are in proper working order.
Whether your u-joint is sealed or lubricated will depend on the make and model of your vehicle. When your vehicle is off-road, you need to install lubricable U-joints for durability and longevity. A new driveshaft or derailleur will cost more than a U-joint. Also, if you don’t have a good understanding of how to replace them, you may need to do some transmission work on your vehicle.
When replacing the U-joint on the drive shaft, be sure to choose an OEM replacement whenever possible. While you can easily repair or replace the original head, if the u-joint is not lubricated, you may need to replace it. A damaged gimbal joint can cause problems with your car’s transmission or other critical components. Replacing your car’s U-joint early can ensure its long-term performance.
Another option is to use two CV joints on the drive shaft. Using multiple CV joints on the drive shaft helps you in situations where alignment is difficult or operating angles do not match. This type of driveshaft joint is more expensive and complex than a U-joint. The disadvantages of using multiple CV joints are additional length, weight, and reduced operating angle. There are many reasons to use a U-joint on a drive shaft.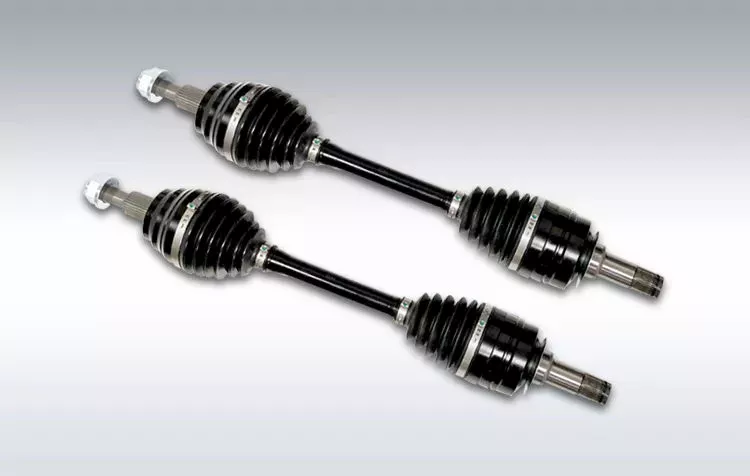
maintenance interval
Checking U-joints and slip joints is a critical part of routine maintenance. Most vehicles are equipped with lube fittings on the driveshaft slip joint, which should be checked and lubricated at every oil change. CZPT technicians are well-versed in axles and can easily identify a bad U-joint based on the sound of acceleration or shifting. If not repaired properly, the drive shaft can fall off, requiring expensive repairs.
Oil filters and oil changes are other parts of a vehicle’s mechanical system. To prevent rust, the oil in these parts must be replaced. The same goes for transmission. Your vehicle’s driveshaft should be inspected at least every 60,000 miles. The vehicle’s transmission and clutch should also be checked for wear. Other components that should be checked include PCV valves, oil lines and connections, spark plugs, tire bearings, steering gearboxes and brakes.
If your vehicle has a manual transmission, it is best to have it serviced by CZPT’s East Lexington experts. These services should be performed every two to four years or every 24,000 miles. For best results, refer to the owner’s manual for recommended maintenance intervals. CZPT technicians are experienced in axles and differentials. Regular maintenance of your drivetrain will keep it in good working order.


editor by czh 2023-01-12